Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells
- PMID: 28508895
- PMCID: PMC5440838
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15287
Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 8;9(1):4109. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06613-3. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30294002 Free PMC article.
Abstract
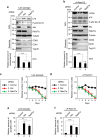
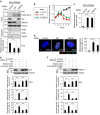
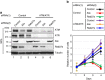
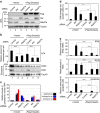
Emerging evidence is revealing that exosomes contribute to many aspects of physiology and disease through intercellular communication. However, the biological roles of exosome secretion in exosome-secreting cells have remained largely unexplored. Here we show that exosome secretion plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis in exosome-secreting cells. The inhibition of exosome secretion results in the accumulation of nuclear DNA in the cytoplasm, thereby causing the activation of cytoplasmic DNA sensing machinery. This event provokes the innate immune response, leading to reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent DNA damage response and thus induce senescence-like cell-cycle arrest or apoptosis in normal human cells. These results, in conjunction with observations that exosomes contain various lengths of chromosomal DNA fragments, indicate that exosome secretion maintains cellular homeostasis by removing harmful cytoplasmic DNA from cells. Together, these findings enhance our understanding of exosome biology, and provide valuable new insights into the control of cellular homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


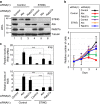
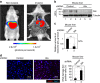
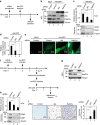
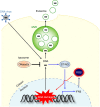
References
-
- Campisi J. & d'Adda di Fagagna F. Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 729–740 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Takahashi A. et al. Mitogenic signalling and the p16INK4a-Rb pathway cooperate to enforce irreversible cellular senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 1291–1297 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

