Cinacalcet in hyperparathyroidism management after pediatric renal transplantation
- PMID: 28508965
- PMCID: PMC5413752
- DOI: 10.1007/s13730-015-0211-0
Cinacalcet in hyperparathyroidism management after pediatric renal transplantation
Abstract
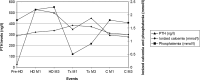
Secondary hyperparathyroidism is often associated with end stage renal disease; even after renal transplantation, hyperparathyroidism may persist, and is responsible for hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia and elevated parathyroid hormone (iPTH) levels. Parathyroid hyperplasia is frequently associated with persistent hyperparathyroidism, and may require a surgical treatment. Here, we report hyperparathyroidism along with parathyroid hyperplasia in a 7-year-old child, which persisted after renal transplant. Calcitonin and pamidronate failed to decrease serum calcium levels; clodronate was also inefficient. Cinacalcet therapy normalized serum calcium and phosphorus levels, and decreased iPTH levels in 3 months; a severe parathyroid hyperplasia was also corrected under calcimimetic therapy. In conclusion, we report in a child that hypercalcemia associated with secondary hyperparathyroidism can be corrected with cinacalcet after pediatric renal transplantation. We also show that parathyroid hyperplasia can regress under calcimimetic therapy in a transplanted child, making surgery unnecessary.
Keywords: Cinacalcet; Hyperparathyroidism; Kidney; Transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources