Prominent hyperplasia of renin-producing juxtaglomerular apparatus after chronic and complete blockade of the renin-angiotensin system in adult IgA nephropathy
- PMID: 28509110
- PMCID: PMC5411639
- DOI: 10.1007/s13730-015-0177-y
Prominent hyperplasia of renin-producing juxtaglomerular apparatus after chronic and complete blockade of the renin-angiotensin system in adult IgA nephropathy
Abstract
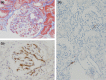
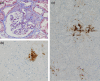
Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) hyperplasia rarely happened in renal biopsy and has been controversial clinically, because synthesis and secretion of renin were susceptible to the effect of clinical condition and medication. Here we present the case of a 39-year-old who got JGA hyperplasia of IgA nephropathy (IgAN) after long-term inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) with an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB), and a direct renin inhibitor (DRI) in combination with a diuretic. He was diagnosed with IgAN in his first renal biopsy, and was treated with supra-maximal dosages of ARB, DRI and a diuretic. In the second biopsy, because of the massive proteinuria and occurrence of steroid-induced diabetes, it was revealed that the area and the number of JGA cells were strikingly increased in observed glomeruli. Immunohistopathologically, the both specimens were stained by human renin antibody. The hyperplastic JG cells contained a large amount of renin granules. Putative renin granules were observed in some interstitial cells adjacent to an afferent arteriole by electron microscopy. The increasing response of renin granules co-localized in prominent JGA hyperplasia should be worried while physicians treat hypertensive patients with potent RAS inhibitors and diuretics even though they have diabetes. This is the first report showing a clinical course of forming prominent JGA hyperplasia directly after a full combination of RAS inhibitors and diuretics in adult IgA nephropathy.
Keywords: IgA nephropathy; Juxtaglomerular apparatus; Renin-angiotensin system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Granular juxtaglomerular cells and prorenin synthesis in mice treated with enalapril.J Hypertens. 1990 Mar;8(3):229-38. J Hypertens. 1990. PMID: 2159503
-
Ultrastructural juxtaglomerular cell changes in normotensive rats treated with quinapril, an inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme.Toxicol Pathol. 1990;18(3):396-406. doi: 10.1177/019262339001800306. Toxicol Pathol. 1990. PMID: 2267499
-
Increased expression of renin in chronic allograft nephropathy.Transplant Proc. 2005 Jun;37(5):2131-4. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.05.001. Transplant Proc. 2005. PMID: 15964360
-
Quantitative estimation of renin-containing cells in the juxtaglomerular apparatus in Bartter's and pseudo-Bartter's syndromes.Pathol Int. 2000 Feb;50(2):166-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.2000.01027.x. Pathol Int. 2000. PMID: 10792778 Review.
-
Effects of renin-angiotensin system inhibition on end-organ protection: can we do better?Clin Ther. 2007 Sep;29(9):1803-24. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.09.019. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18035185 Review.
References
-
- Schweda F, Friis U, Wagner C, Skott O, Kurtz A. Renin release. Physiology. 2007;22(310–31):9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

