Treatment of a recurrent renal artery stenosis and stent fracture using a drug eluting stent in a pediatric patient
- PMID: 28509158
- PMCID: PMC5413738
- DOI: 10.1007/s13730-015-0182-1
Treatment of a recurrent renal artery stenosis and stent fracture using a drug eluting stent in a pediatric patient
Abstract
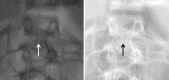
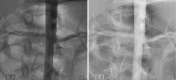
Renal artery obstruction is uncommon in the pediatric population and therefore represents a challenging diagnosis to ascertain and treat. While angioplasty and surgery have been used to treat it, stent implantation has been left mainly for adult use. In the following paper, we expose the case of an 8-year-old female who presented with severe arterial hypertension. Initially, the patient was evaluated and up to 5 antihypertensive medications were started. After complete evaluation, she was found to have severe right renal artery distal and proximal stenosis. She underwent recurrent angioplasties and then a bare metal stent (BMS) implantation, due to recurrence of stenosis. The original BMS developed a circumferential fracture, leading to a second stent implant, this time using a drug eluting stent (DES). She has been stable for 8 years since the last intervention, although using 2 antihypertensive medications. The use of BMS and DES may add another tool in the armamentarium of the pediatric interventionist to treat these children with recurrent stenosis that fail angioplasty.
Keywords: Hypertension; Pediatrics; Renal artery; Stenosis; Stent.
Figures

References
-
- Gruskin AB et al. Mechanisms of hypertension in childhood diseases. In: Barrat TM et al, editors. Pediatric nephrology, 4th ed. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1998, pp 1009–1011.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

