Graft versus host disease-dependent renal dysfunction after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 28509199
- PMCID: PMC5411568
- DOI: 10.1007/s13730-014-0118-1
Graft versus host disease-dependent renal dysfunction after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
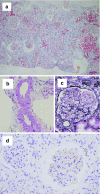
Nephropathy is an important complication in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) wherein multifactorial causes, i.e., radiation, drug toxicity, graft versus host disease (GVHD), are thought to contribute renal dysfunction. Here, we report a 10-year-old boy with high-risk acute myelocytic leukemia and severe but partially reversible renal dysfunction. The patient initially received umbilical cord blood transplantation (UCBT) with CY 120 mg/kg and kidney unshielded 12 Gy of total body irradiation. After the leukemic relapse, he received allogenic bone marrow transplantation (BMT) 270 days after the first transplantation. Two months later, his renal function started to deteriorate and urinary protein increased gradually to 1 g/day. Four months after BMT, by the symptoms of severe GVHD, the dose of tacrolimus, utilized to avoid GVHD, was increased although his serum Cre level elevated to 2.97 mg/dL. Serum Cre level improved to 2.0 mg/dL paralleled with GVHD improvement. Renal histological findings showed severe interstitial edema, features of thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), and C4d deposition along the glomerular capillaries and peritubular capillaries. We suggested that control of GVHD had benefitted to ameliorate renal function of the patient. Treatment for GVHD improved renal dysfunction and TMA of our patients. Moreover, renal biopsy was powerful to elucidate the exact origin of renal dysfunction after HSCT.
Keywords: Bone marrow transplant nephropathy; Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity; Interstitial edema; Mesangiolysis; Thrombotic microangiopathy; Total body irradiation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Renal thrombotic microangiopathy associated with chronic humoral graft versus host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Pathol Int. 2011 Jan;61(1):34-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2010.02608.x. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Pathol Int. 2011. PMID: 21166941
-
Thrombotic Microangiopathy With Granulomatosis Interstitial Nephritis in an Allogenic Bone Marrow Transplant Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.J Hematol. 2017 Sep;6(2-3):52-58. doi: 10.14740/jh326e. Epub 2017 Jul 20. J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 32300393 Free PMC article.
-
Renal thrombotic microangiopathy associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Pathol Int. 2011 Sep;61(9):518-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2011.02704.x. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Pathol Int. 2011. PMID: 21884301
-
Renal dysfunction following bone marrow transplantation.J Nephrol. 2017 Apr;30(2):201-209. doi: 10.1007/s40620-016-0345-y. Epub 2016 Sep 2. J Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27589851 Review.
-
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2016 Jan;22(1):12-20. doi: 10.1177/1076029615598221. Epub 2015 Aug 2. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2016. PMID: 26239316 Review.
Cited by
-
Case report: Nephrotic syndrome and portal hypertensive ascites after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a rare manifestation of chronic graft-versus-host disease.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 16;15:1464616. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1464616. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39478870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakai K, Usui J, Kai H, Hagiwara M, Morito N, Saito C, Yoh K, Tsuruoka W, Hirayama K, Aita K, Nagata M, Yamagata K. Secondary membranous glomerulonephritis associated with recipient residual lymphoma cells after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2009;13:174–178. doi: 10.1007/s10157-008-0120-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cilley J, Winter JN. Radioimmunotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation for the treatment of B-cell lymphomas. Haematologica. 2006;91:113–120. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

