Monitoring with serum SP-A, SP-D, and KL-6 in a patient with interstitial pneumonia complicated with ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis
- PMID: 28509235
- PMCID: PMC5413670
- DOI: 10.1007/s13730-013-0074-1
Monitoring with serum SP-A, SP-D, and KL-6 in a patient with interstitial pneumonia complicated with ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis
Abstract
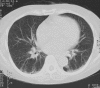
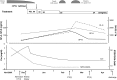
A 69-year-old woman was admitted to hospital, complaining of fatigue and dry cough. Her renal function deteriorated rapidly, and the laboratory findings showed elevated myeloperoxidase-specific anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA). Renal biopsy examination revealed crescentic glomerulonephritis (pauci-immune type), and linear opacities and a honeycomb appearance in both lower lobes was evident on the chest computed tomography scan. The patient was diagnosed as having ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis complicated with mild interstitial pneumonia (IP). Treatment with methylprednisolone pulse therapy improved both her renal function and IP, but her lung lesions worsened during the course of tapering the prednisolone doses. After careful observation, her IP improved gradually without specific treatment. Worsening or improvement of her lung lesions was accompanied by changes in the serological markers of IP, namely, surfactant protein-A, surfactant protein-D, and KL-6. We found that monitoring these markers was helpful in diagnosing and managing IP in our patient with ANCA-associated vasculitis.
Keywords: Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; Interstitial pneumonia; KL-6; Surfactant protein-A; Surfactant protein-D.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Two autopsy cases of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis manifested after contrast medium use].Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2004;46(4):365-70. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2004. PMID: 16773800 Japanese.
-
[A case of MPO ANCA associated glomerulonephritis with interstitial pneumonitis complicated with lung tuberculosis and pericarditis].Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2000 Oct;42(7):591-6. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2000. PMID: 11155703 Japanese.
-
[Two cases of pulmonary disease with perinuclear anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2001 Apr;39(4):250-5. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11481823 Japanese.
-
[A case of myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-positive crescentic glomerulonephritis induced by propylthiouracil (PTU)].Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1997 Jul;39(5):517-22. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1997. PMID: 9283219 Review. Japanese.
-
[A case with rheumatoid arthritis complicated with ANCA-associated vasculitis].Ryumachi. 1998 Oct;38(5):741-6. Ryumachi. 1998. PMID: 9852752 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
KL-6 in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Patients with and without ILD: A Machine Learning Approach.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jan 8;11(1):94. doi: 10.3390/biology11010094. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053092 Free PMC article.
-
Poor prognostic factors for relapse of interstitial lung disease in microscopic polyangiitis: the Japanese multicentre REVEAL cohort study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Dec 19;26(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03453-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39702378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosch X, Mirapeix E, Font J, Cervera R, Ingelmo M, Khamashta MA, et al. Anti-myeloperoxidase autoantibodies in patients with necrotizing glomerular and alveolar capillaritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992;20:231–239. - PubMed
-
- Mason RJ, Greene K, Voelker DR. Surfactant protein A and surfactant protein D in health and disease. Am J Physiol. 1998;275(1 Pt 1):L1–L13. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi H, Fujishima T, Koba H, Murakami S, Kurokawa K, Shibuya Y, et al. Serum surfactant proteins A and D as prognostic factors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and their relationship to disease extent. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:1109–1114. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.162.3.9910080. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ohnishi H, Yokoyama A, Kondo K, Hamada H, Abe M, Nishimura K, et al. Comparative study of KL-6, surfactant protein-A, surfactant protein-D, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 as serum markers for interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:378–381. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.165.3.2107134. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

