A case of acute interstitial nephritis and granulomatous hepatitis induced by ingesting quinine
- PMID: 28509275
- PMCID: PMC5413713
- DOI: 10.1007/s13730-014-0143-0
A case of acute interstitial nephritis and granulomatous hepatitis induced by ingesting quinine
Abstract
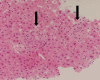
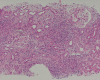
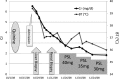
Quinine is used for the treatment of malarial infection, though not in common use. It is especially valuable for the parenteral treatment of severe illness owing to drug-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum. Quinine is also known to occasionally cause acute renal failure (ARF). Although quinine is listed in some reviews as a cause of acute interstitial nephritis, most cases of quinine-associated acute renal failure have been attributed to the hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS). Only two cases of acute renal failure due to acute interstitial nephritis associated with quinine have been reported [1, 2]. To our knowledge, there have been 6 reported cases of quinine-induced hepatic granuloma [3-8]. We report a case of quinine-induced acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) along with granulomatous hepatitis, both of which were confirmed on biopsy. A 50-year-old Nigerian man was admitted to the hospital with complaints of fever and general fatigue. He had been prescribed quinine as an antimalarial drug in a Nigerian hospital. The patient was febrile and showed nonoliguric ARF and liver dysfunction. In this case, liver injury showed gradual and spontaneous resolution after discontinuing quinine, and ARF resolved after treatment with oral prednisolone.
Keywords: Acute interstitial nephritis; Acute renal failure; Biopsy; Hepatic granuloma; Quinine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Azithromycin-Induced, Biopsy-Proven Acute Interstitial Nephritis in an Adult Successfully Treated with Low-Dose Corticosteroids.Pharmacotherapy. 2015 Nov;35(11):e169-74. doi: 10.1002/phar.1660. Pharmacotherapy. 2015. PMID: 26598102
-
Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug induced acute granulomatous interstitial nephritis.BMC Res Notes. 2015 Dec 16;8:793. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1788-2. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 26674186 Free PMC article.
-
Levofloxacin-induced granulomatous interstitial nephritis.Am J Kidney Dis. 2003 Feb;41(2):E7. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2003.50064. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003. PMID: 12552523
-
Quinine-associated acute interstitial nephritis.Am J Kidney Dis. 1994 Aug;24(2):211-4. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(12)80184-3. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994. PMID: 8048427 Review.
-
Collapsing Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis with Acute Interstitial Nephritis Associated with Plasmodium Falciparum: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Am J Case Rep. 2019 Oct 27;20:1576-1580. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.917722. Am J Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31655844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Allopurinol-Induced Granulomatous Hepatitis: A Case Report and Review of Literature.J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2017 Sep 8;5(3):2324709617728302. doi: 10.1177/2324709617728302. eCollection 2017 Jul-Sep. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29082266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lins RL, Verpooten GA, De Clerck DS, De Broe ME. Urinary indices in acute interstitial nephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1986;26:131–133. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

