Biosensor binding data and its applicability to the determination of active concentration
- PMID: 28510014
- PMCID: PMC5418478
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-016-0219-5
Biosensor binding data and its applicability to the determination of active concentration
Abstract
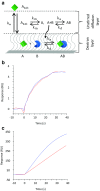
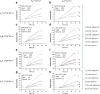
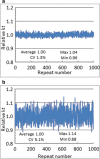
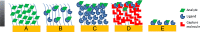
Protein concentration data are required for understanding protein interactions and are a prerequisite for the determination of affinity and kinetic properties. It is vital for the judgment of protein quality and for monitoring the effect of therapeutic agents. Protein concentration values are typically obtained by comparison to a standard and derived from a standard curve. The use of a protein standard is convenient, but may not give reliable results if samples and standards behave differently. In other cases, a standard preparation may not be available and has to be established and validated. Using surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensors, an alternative concentration method is possible. This method is called calibration-free concentration analysis (CFCA); it generates active concentration data directly and without the use of a standard. The active concentration of a protein is defined through its interaction with its binding partner. This concentration can differ from the total protein concentration if some protein fraction is incapable of binding. If a protein has several different binding sites, active concentration data can be established for each binding site using site-specific interaction partners. This review will focus on CFCA analysis. It will reiterate the theory of CFCA and describe how CFCA has been applied in different research segments. The major part of the review will, however, try to set expectations on CFCA and discuss how CFCA can be further developed for absolute and relative concentration measurements.
Keywords: Biomarker; CFCA; Protein quality; SPR; Simulation; Vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The author is employed by GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences AB, the provider of Biacore™ systems.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Abdiche YN, Yeung YA, Chaparro-Riggers J, Barman I, Strop P, Chin SM, Pham A, Bolton G, McDonough D, Lindquist K, Pons J, Rajpal K. The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) binds independently to both sites of the IgG homodimer with identical affinity. MAbs. 2015;7(2):331–343. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1008353. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

