Design and development of genetically encoded fluorescent sensors to monitor intracellular chemical and physical parameters
- PMID: 28510054
- PMCID: PMC4884202
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-016-0195-9
Design and development of genetically encoded fluorescent sensors to monitor intracellular chemical and physical parameters
Abstract
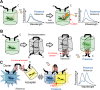
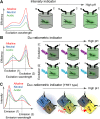
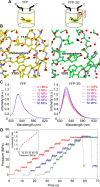
Over the past decades many researchers have made major contributions towards the development of genetically encoded (GE) fluorescent sensors derived from fluorescent proteins. GE sensors are now used to study biological phenomena by facilitating the measurement of biochemical behaviors at various scales, ranging from single molecules to single cells or even whole animals. Here, we review the historical development of GE fluorescent sensors and report on their current status. We specifically focus on the development strategies of the GE sensors used for measuring pH, ion concentrations (e.g., chloride and calcium), redox indicators, membrane potential, temperature, pressure, and molecular crowding. We demonstrate that these fluroescent protein-based sensors have a shared history of concepts and development strategies, and we highlight the most original concepts used to date. We believe that the understanding and application of these various concepts will pave the road for the development of future GE sensors and lead to new breakthroughs in bioimaging.
Keywords: Fluorescent measurement; Fluorescent protein; Genetically encoded; Green fluorescent protein; Intracellular sensor; Probe design.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
Arno Germond declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Hideaki Fujita declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Taro Ichimura declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Tomonobu M. Watanabe declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

