Seeing the light with BLUF proteins
- PMID: 28510088
- PMCID: PMC5425820
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-017-0258-6
Seeing the light with BLUF proteins
Abstract
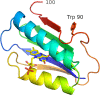
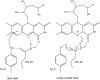
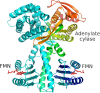
First described about 15 years ago, BLUF (Blue Light Using Flavin) domains are light-triggered switches that control enzyme activity or gene expression in response to blue light, remaining activated for seconds or even minutes after stimulation. The conserved, ferredoxin-like fold holds a flavin chromophore that captures the light and somehow triggers downstream events. BLUF proteins are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes and have a variety of architectures and oligomeric forms, but the BLUF domain itself seems to have a well-preserved structure and mechanism that have been the focus of intense study for a number of years. Crystallographic and NMR structures of BLUF domains have been solved, but the conflicting models have led to considerable debate about the atomic details of photo-activation. Advanced spectroscopic and computational methods have been used to analyse the early events after photon absorption, but these too have led to widely differing conclusions. New structural models are improving our understanding of the details of the mechanism and may lead to novel tailor-made tools for optogenetics.
Keywords: Allostery; Flavin; Optogenetics; Photo-activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Sam-Yong Park declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Jeremy R. H. Tame declares that he has no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Barends TRM, Hartmann E, Griese JJ et al (2009) Structure and mechanism of a bacterial light-regulated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Nature 459:1015–1018 - PubMed
-
- Bonetti C, Stierl M, Mathes T et al (2009) The role of key amino acids in the photoactivation pathway of the Synechocystis Slr 1694 BLUF domain. Biochemistry 48:11458–11469 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

