Effectiveness of community-based peer support for mothers to improve their breastfeeding practices: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28510603
- PMCID: PMC5433692
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177434
Effectiveness of community-based peer support for mothers to improve their breastfeeding practices: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
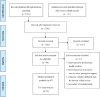
Methods: We searched for evidence regarding community-based peer support for mothers in databases, such as PubMed/MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library, CINAHL, Web of Science, SocINDEX, and PsycINFO. We selected three outcome variables for breastfeeding practices, namely, exclusive breastfeeding duration, breastfeeding within the first hour of life, and prelacteal feeding. We conducted meta-analyses of the included randomized controlled trials and quasi-experimental studies.
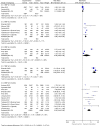
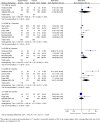
Results: For our review, we selected 47 articles for synthesis out of 1,855 retrieved articles. In low- and middle-income countries, compared to usual care, community-based peer support increased exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months (RR: 1.90, 95% CI: 1.62-2.22), at 5 months (RR: 9.55, 95% CI: 6.65-13.70) and at 6 months (RR: 3.53, 95% CI: 2.49-5.00). In high-income countries, compared to usual care, peer support increased exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months (RR: 2.61, 95% CI: 1.15-5.95). In low- and middle-income countries, compared to usual care, peer support increased the initiation of breastfeeding within the first hour of life (RR: 1.51, 95% CI: 1.04-2.21) and decreased the risk of prelacteal feeding (RR: 0.38, 95% CI: 0.33-0.45).
Conclusions: Community-based peer support for mothers is effective in increasing the duration of exclusive breastfeeding, particularly for infants aged 3-6 months in low- and middle-income countries. Such support also encourages mothers to initiate breastfeeding early and prevents newborn prelacteal feeding.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Victora CG, Bahl R, Barros AJ, França GV, Horton S, Krasevec J, et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):475–90. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01024-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Black RE, Allen LH, Bhutta ZA, Caulfield LE, de Onis M, Ezzati M, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition: global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet. 2008;371(9608):243–60. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61690-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Edmond KM, Zandoh C, Quigley MA, Amenga-Etego S, Owusu-Agyei S, Kirkwood BR. Delayed breastfeeding initiation increases risk of neonatal mortality. Pediatrics. 2006;117(3):e380–6. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-1496 - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Protecting, promoting and supporting breast-feeding: the special role of maternity services A Joint WHO/UNICEF Statement. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1989.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

