Chemical and pharmacological investigation of micropropagated Hygrophila pogonocalyx produced from leaf explants
- PMID: 28510887
- PMCID: PMC5430379
- DOI: 10.1186/1999-3110-54-51
Chemical and pharmacological investigation of micropropagated Hygrophila pogonocalyx produced from leaf explants
Abstract
Background: An optimized method for indirect shoot organogenesis from the leaf explants of Hygrophila pogonocalyx, a rare and endemic species in Taiwan, was developed to supply enough quantity of plant materials for the first chemical and pharmacological investigation.
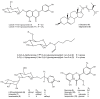
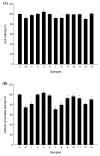
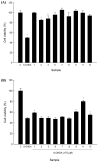
Results: Incubation of the young leaves on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with 6-benzylaminopurine (0.5 mg/l) and indole-3-acetic acid (0.1 mg/l) resulted in the best multiplication rate for organogenesis. The average number of adventitious buds per leaf was 22.8 ± 1.9 after 8-week culture. The adventitious buds rooted and developed into plantlets when cultured simply on MS medium. Using this protocol, up to 37,600 plants were produced from a single leaf explant in one year. From the ethanol extract of the leaves of this micropropagated plant, 13 compounds were isolated and identified, including two flavones (1, 11), four flavonols (9, 10, 12, and 13), three phenylethanoid glycosides (6-8), two alkylated glycosides (2-3), and two steroids (4-5). Of these, acteoside (7) exhibited anti-tyrosinase activity in human epidermal melanocytes and luteolin 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (11) exhibited the greatest neurocytoprotective activity.
Conclusions: The method, indirect shoot organogenesis from leaf explants of H. pogonocalyx, could be developed to supply enough quantity of plant materials for the chemical and pharmacological investigation. In the present study, the isolated active compounds may develop for whitening agents or treating neurodegenerative diseases in the future.
Keywords: Anti-melanogenesis; Constituents; Hygrophila pogonocalyx; Indirect shoot organogenesis from leaf explants; Neurocytoprotection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mass propagation of Plectranthus bourneae Gamble through indirect organogenesis from leaf and internode explants.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2016 Jan;22(1):143-51. doi: 10.1007/s12298-016-0337-3. Epub 2016 Jan 16. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2016. PMID: 27186028 Free PMC article.
-
Growth optimization and organogenesis of Gerbera jamesonii Bolus ex. Hook f. in vitro.Pak J Biol Sci. 2008 Jun 1;11(11):1449-54. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2008.1449.1454. Pak J Biol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18817245
-
Indirect shoot organogenesis from leaf explants of Adhatoda vasica Nees.Springerplus. 2014 Nov 3;3:648. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-648. eCollection 2014. Springerplus. 2014. PMID: 25485191 Free PMC article.
-
High frequency direct shoot organogenesis of leaf explants and a comparative evaluation of phytochemicals, antioxidant potential of wild vs. in vitro plant extracts of Lysimachia laxa.3 Biotech. 2017 Aug;7(4):274. doi: 10.1007/s13205-017-0907-2. Epub 2017 Aug 2. 3 Biotech. 2017. PMID: 28794929 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient and reproducible indirect shoot regeneration from female leaf explants of Simmondsia chinensis, a liquid-wax producing shrub.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2015 Apr;21(2):293-9. doi: 10.1007/s12298-015-0279-1. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2015. PMID: 25964722 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adventitious root cultures of Decalepis salicifolia for the production of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde, a vanillin isomer flavor metabolite.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Apr;105(8):3087-3099. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11262-6. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33829315
-
Chemical Constituents and Anticancer Activities of the Extracts from Phlomis × commixta Rech. f. (P. cretica × P. lanata).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 9;25(2):816. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020816. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255889 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylcholinesterase-Inhibition and Antibacterial Activity of Mondia whitei Adventitious Roots and Ex vitro-Grown Somatic Embryogenic-Biomass.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 3;7:335. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00335. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27752244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balaraju K, Agastian P, Preetamraj JP, Arokiyaraj S, Ignacimuthu S. Micropropagation of Vitex agnus-castus, (Verbenaceae) - a valuable medicinal plant. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant. 2008;44:436–441. doi: 10.1007/s11627-008-9155-9. - DOI
-
- Bibu KJ, Joy AD, Mercey KA. Therapeutic effect of ethanolic extract of Hygrophila spinosa T. Anders on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 2010;48:911–917. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

