Functional characterization of the N-terminal and C-terminal domains of a sesame group II phytocystatin
- PMID: 28510930
- PMCID: PMC5432954
- DOI: 10.1186/1999-3110-55-18
Functional characterization of the N-terminal and C-terminal domains of a sesame group II phytocystatin
Abstract
Background: Phytocystatins are natural inhibitors of cysteine protease, and may regulate endo- or exo-genous proteolytic activities in plants. They are classified into Group I and II differing by the presence of C-terminal extension of Group II. A cDNA fragment encoding a Group II phytosystatin, SiCYS was previously obtained from sesame seeds.
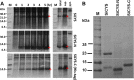
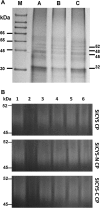
Results: SiCYS as well as its two structural domains, N-terminal and C-terminal domains (SiCYS-N and SiCYS-C), was expressed in Escherichia coli. The recombinant SiCYS and SiCYS-N showed inhibitory activity against papain. The K i values of SiCYS and SiCYS-N were ~1.9 ×10-8 M and ~7.9 ×10-8 M, respectively. All the three recombinants possessed comparable ability to inhibit spore germination of Trichoderma reesei, Aspergillus sydowii, and Helminthosporium sesamum. Similar protein profile including proteases in germinating seeds was found in proteins purified by the SiCYS, SiCYS-N or SiCYS-C coupling affinity column.
Conclusion: SiCYS exhibited more effective papain-inhibitory activity than SiCYS-N; while SiCYS-C had almost no inhibitory activity. All displayed similar antifungal activities indicating that there is no correlation between antifungal and papain-inhibitory activities. Structural and sequence analyses suggest that the C-terminal domain of SiCYS may be originated from gene duplication to enhance its inhibitory activity.
Keywords: Antifungal; Cysteine protease; Papain; Phytocystatin; Sesamun indicum.
Figures



References
-
- Abe K, Kondo H, Watanabe H, Emori Y, Arai S. Oryzacystatins as the first well-defined cystatins of plant origin and their target proteinases in rice seeds. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1991;50:637–641. - PubMed
-
- Aguiar JM, Franco OL, Rigden DJ, Bloch C, Monteiro A, Flores VM, Jacinto T, Xavier-Filho J, Oliveira AEA, Grossi-de-Sá MF, Fernandes KVS. Molecular modeling and inhibitory activity of cowpea cystatin against bean bruchid pests. Proteins: Struc Func Bioinform. 2006;63(3):662–670. doi: 10.1002/prot.20901. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Botella MA, Xu Y, Prabha TN, Zhao Y, Narasimhan ML, Wilson KA, Nielsen SS, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM. Differential expression of soybean cysteine proteinase inhibitor genes during development and in response to wounding and methyl jasmonate. Plant Physiol. 1996;112(3):1201–1210. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.3.1201. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

