The Effect of Chunghyul-Dan on Hyperventilation-Induced Carbon Dioxide Reactivity of the Middle Cerebral Artery in Normal Subjects: A Dose-Dependent Study
- PMID: 28512500
- PMCID: PMC5415863
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/4567217
The Effect of Chunghyul-Dan on Hyperventilation-Induced Carbon Dioxide Reactivity of the Middle Cerebral Artery in Normal Subjects: A Dose-Dependent Study
Abstract
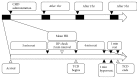
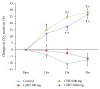
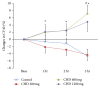
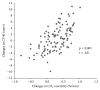
Background. This study was conducted to show the prompt effect of chunghyul-dan (CHD) on cerebral hemodynamics in order to provide evidence for its use in stroke prevention. Methods. Hyperventilation-induced CO2 reactivity of the middle cerebral artery was measured in 12 healthy male volunteers (mean age: 26.3 ± 1.1 years) using transcranial Doppler sonography. All subjects were examined before and for 3 hours after administration, with an interval of 1 week between measurements. Results. Compared to baseline, the CO2 reactivity of the middle cerebral artery increased significantly at 2 and 3 hours after the administration of CHD (600 mg and 1200 mg). The mean blood pressure and heart rate did not vary from the baseline values in all groups. Conclusion. These data suggest that CHD administration (especially 600 mg) immediately improves cerebral blood flow.
Figures
References
-
- Jung W. S., Cho J., In K., et al. Chunghyul-dan acts as an anti-Inflammatory agent in endothelial cells by regulating gene expression. Animal Cells and Systems. 2010;14(4):275–282. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2010.525824. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

