Case of Primary Leptomeningeal Lymphoma Presenting with Papilloedema and Characteristics of Pseudotumor Syndrome
- PMID: 28512506
- PMCID: PMC5417092
- DOI: 10.1080/01658107.2017.1292533
Case of Primary Leptomeningeal Lymphoma Presenting with Papilloedema and Characteristics of Pseudotumor Syndrome
Abstract
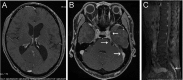
The authors describe an immunocompetent, 50-year-old man who complained of a daily transient blurring of his vision with bilateral papilloedema. His visual acuity was 20/20 OU, and the blind spot was enlarged bilaterally. There was intracranial hypertension, but imaging for systemic and brain tumours were negative. These findings suggested a diagnosis of the pseudotumor syndrome. However, MRI showed leptomeningeal enhancement, and acetazolamide successfully resolved his visual symptoms and papilloedema. Cytology and flow cytometry of the CSF led to the final diagnosis of primary leptomeningeal lymphoma (PLML). Clinicians need to be aware that a case of PLML may be misdiagnosed as peudotumor cerebri.
Keywords: Acetazolamide; cerebrospinal fluid cytology; papilloedema; primary leptomeningeallymphoma; pseudotumor cerebri; pseudotumor syndrome; transient visual obscuration.
Figures


References
-
- Olson JE, Janney CA, Rao RD, Cerhan JR, Kurtin PJ, Schiff D, Kaplan RS, O’Neill BP.. The continuing increase in the incidence of primary central nervous system non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results analysis. Cancer 2002;95:1504–1510. - PubMed
-
- Sagoo MS, Mehta H, Swampillai AJ, Cohen VM, Amin SZ, Plowman PN, Lightman S.. Primary intraocular lymphoma. Surv Ophthalmol 2014;59:503–516. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
