A Study on Immersion and Presence of a Portable Hand Haptic System for Immersive Virtual Reality
- PMID: 28513545
- PMCID: PMC5470817
- DOI: 10.3390/s17051141
A Study on Immersion and Presence of a Portable Hand Haptic System for Immersive Virtual Reality
Abstract
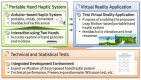
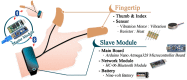
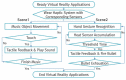
This paper proposes a portable hand haptic system using Leap Motion as a haptic interface that can be used in various virtual reality (VR) applications. The proposed hand haptic system was designed as an Arduino-based sensor architecture to enable a variety of tactile senses at low cost, and is also equipped with a portable wristband. As a haptic system designed for tactile feedback, the proposed system first identifies the left and right hands and then sends tactile senses (vibration and heat) to each fingertip (thumb and index finger). It is incorporated into a wearable band-type system, making its use easy and convenient. Next, hand motion is accurately captured using the sensor of the hand tracking system and is used for virtual object control, thus achieving interaction that enhances immersion. A VR application was designed with the purpose of testing the immersion and presence aspects of the proposed system. Lastly, technical and statistical tests were carried out to assess whether the proposed haptic system can provide a new immersive presence to users. According to the results of the presence questionnaire and the simulator sickness questionnaire, we confirmed that the proposed hand haptic system, in comparison to the existing interaction that uses only the hand tracking system, provided greater presence and a more immersive environment in the virtual reality.
Keywords: Arduino-based sensor; hand haptic system; immersion; immersive virtual reality; interaction; presence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Slater M., Steed A. A virtual presence counter. Presence Teleoper. Virtual Environ. 2000;9:413–434. doi: 10.1162/105474600566925. - DOI
-
- Slater M. Measuring Presence: A Response to the Witmer and Singer Presence Questionnaire. Presence Teleoper. Virtual Environ. 1999;8:560–565. doi: 10.1162/105474699566477. - DOI
-
- Slater M. Presence and the sixth sense. Presence Teleoper. Virtual Environ. 2002;11:435–439. doi: 10.1162/105474602760204327. - DOI
-
- Slater M., Sanchez-Vives M.V. Enhancing our lives with immersive virtual reality. Front. Robot. AI. 2016;3 doi: 10.3389/frobt.2016.00074. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

