Protective effects of dioscin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via the microRNA-34a/sirtuin 1 signalling pathway
- PMID: 28514495
- PMCID: PMC5513863
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13862
Protective effects of dioscin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via the microRNA-34a/sirtuin 1 signalling pathway
Erratum in
-
CORRECTION.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Dec;176(24):4787. doi: 10.1111/bph.14940. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31950489 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and purpose: Dioscin exhibits a range of pharmacological actions but little is known of its effects on cisplatin (CDDP)-induced nephrotoxicity. Here, we have assessed the effects and the possible mechanisms of dioscin against CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity.
Experimental approach: We used an in vivo model of CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity in rats and mice and, in vitro, cultures of NRK-52E and HK-2 cells. The dual luciferase reporter assay was used to demonstrate modulation, by dioscin, of the targeting of sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) by microRNA (miR)-34a. Molecular docking assays were used to analyse the effects of dioscin with Sirt1, Keap1 and NF-κB.
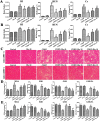
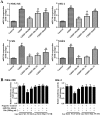
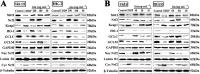
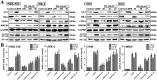
Key results: Dioscin attenuated cell damage in vitro and decreased renal injury in rats and mice, treated with CDDP. In terms of mechanisms, dioscin reversed CDDP-induced up-regulation of miR-34a and thus up-regulated Sirt1 levels. In addition, dioscin altered levels of haem oxygenase 1, glutathione-cysteine ligase subunits (GCLC, GCLM) and Keap1, along with increased nuclear translocation of Nrf2, thus decreasing oxidative stress. Also, dioscin affected levels of AP-1, COX-2, HMGB1, IκB-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α and decreased the ratio of acetylated NF-κB and normal NF-κB, to suppress inflammation. From molecular docking assays, dioscin directly bound to Sirt1, Keap1 and NF-κBp65 by hydrogen bonding and/or hydrophobic interactions.
Conclusions and implications: Our results have linked CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity and the miR-34a/Sirt1 signalling pathway, which was modulated by dioscin. This natural product could be developed as a new candidate to alleviate CDDP-induced renal injury.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures


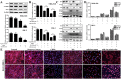
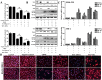

Similar articles
-
Protective effects of dioscin against doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity via adjusting FXR-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation.Toxicology. 2017 Mar 1;378:53-64. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Toxicology. 2017. PMID: 28082111
-
Dioscin alleviates dimethylnitrosamine-induced acute liver injury through regulating apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 Jul;45:193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2016.06.002. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27317992
-
Dioscin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory kidney injury via the microRNA let-7i/TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Sep;111:509-522. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.07.016. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27431331
-
Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: a balance on the knife edge between renoprotection and tumor toxicity.J Biomed Sci. 2019 Mar 13;26(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0518-9. J Biomed Sci. 2019. PMID: 30866950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The anti-cancer activity of Dioscin: an update and future perspective.Med Oncol. 2025 Feb 3;42(3):63. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02572-6. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39899128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Positive and Negative Regulation of Ferroptosis and Its Role in Maintaining Metabolic and Redox Homeostasis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Apr 28;2021:9074206. doi: 10.1155/2021/9074206. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34007410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hybrid Polyketides from a Hydractinia-Associated Cladosporium sphaerospermum SW67 and Their Putative Biosynthetic Origin.Mar Drugs. 2019 Oct 24;17(11):606. doi: 10.3390/md17110606. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31653089 Free PMC article.
-
Astragaloside-IV alleviates high glucose-induced ferroptosis in retinal pigment epithelial cells by disrupting the expression of miR-138-5p/Sirt1/Nrf2.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):8240-8254. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2049471. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35302431 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of dioscin against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via adjusting microRNA-140-5p-mediated myocardial oxidative stress.Redox Biol. 2018 Jun;16:189-198. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.02.026. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 29524841 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Anti-Inflammatory Spirostene-Pyrazole Conjugates by a Consecutive Multicomponent Reaction of Diosgenin with Oxalyl Chloride, Arylalkynes and Hydrazines or Hydrazones.Molecules. 2021 Dec 28;27(1):162. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010162. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arany I, Safirstein RL (2003). Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol 23: 460–464. - PubMed
-
- Basu A, Singha Roy S, Bhattacharjee A, Bhuniya A, Baral R, Biswas J et al. (2016). Vanadium(III)‐l‐cysteine protects cisplatin‐induced nephropathy through activation of Nrf2/HO‐1 pathway. Free Radic Res 50: 39–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

