Protective effects of dioscin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via the microRNA-34a/sirtuin 1 signalling pathway
- PMID: 28514495
- PMCID: PMC5513863
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13862
Protective effects of dioscin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via the microRNA-34a/sirtuin 1 signalling pathway
Erratum in
-
CORRECTION.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Dec;176(24):4787. doi: 10.1111/bph.14940. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31950489 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and purpose: Dioscin exhibits a range of pharmacological actions but little is known of its effects on cisplatin (CDDP)-induced nephrotoxicity. Here, we have assessed the effects and the possible mechanisms of dioscin against CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity.
Experimental approach: We used an in vivo model of CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity in rats and mice and, in vitro, cultures of NRK-52E and HK-2 cells. The dual luciferase reporter assay was used to demonstrate modulation, by dioscin, of the targeting of sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) by microRNA (miR)-34a. Molecular docking assays were used to analyse the effects of dioscin with Sirt1, Keap1 and NF-κB.
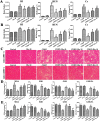
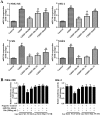
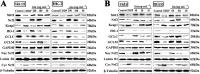
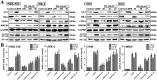
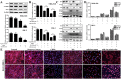
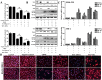
Key results: Dioscin attenuated cell damage in vitro and decreased renal injury in rats and mice, treated with CDDP. In terms of mechanisms, dioscin reversed CDDP-induced up-regulation of miR-34a and thus up-regulated Sirt1 levels. In addition, dioscin altered levels of haem oxygenase 1, glutathione-cysteine ligase subunits (GCLC, GCLM) and Keap1, along with increased nuclear translocation of Nrf2, thus decreasing oxidative stress. Also, dioscin affected levels of AP-1, COX-2, HMGB1, IκB-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α and decreased the ratio of acetylated NF-κB and normal NF-κB, to suppress inflammation. From molecular docking assays, dioscin directly bound to Sirt1, Keap1 and NF-κBp65 by hydrogen bonding and/or hydrophobic interactions.
Conclusions and implications: Our results have linked CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity and the miR-34a/Sirt1 signalling pathway, which was modulated by dioscin. This natural product could be developed as a new candidate to alleviate CDDP-induced renal injury.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures



References
-
- Arany I, Safirstein RL (2003). Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol 23: 460–464. - PubMed
-
- Basu A, Singha Roy S, Bhattacharjee A, Bhuniya A, Baral R, Biswas J et al. (2016). Vanadium(III)‐l‐cysteine protects cisplatin‐induced nephropathy through activation of Nrf2/HO‐1 pathway. Free Radic Res 50: 39–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

