The Dickkopf1-cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 axis creates a novel signalling pathway and may represent a molecular target for cancer therapy
- PMID: 28514532
- PMCID: PMC5727324
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13863
The Dickkopf1-cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 axis creates a novel signalling pathway and may represent a molecular target for cancer therapy
Abstract
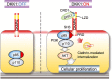
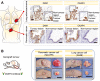
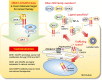
Dickkopf 1 (DKK1) is a secreted protein and antagonizes oncogenic Wnt signalling by binding to the Wnt co-receptor, low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6. DKK1 has also been suggested to regulate its own signalling, associated with tumour aggressiveness. However, the underlying mechanism by which DKK1 promotes cancer cell proliferation has remained to be clarified for a long time. The cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (CKAP4), originally identified as an endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein, was recently found to act as a novel DKK1 receptor. DKK1 stimulates cancer cell proliferation when CKAP4 is expressed on the cell surface membrane. Although there are no tyrosine residues in the intracellular region of CKAP4, CKAP4 forms a complex with PI3K upon the binding of DKK1, leading to the activation of Akt. Both DKK1 and CKAP4 are frequently expressed in pancreatic and lung tumours, and their simultaneous expression is negatively correlated with prognosis. Knockdown of CKAP4 in cancer cells and treatment of mice with the anti-CKAP4 antibody inhibit Akt activity in cancer cells and suppress xenograft tumour formation, suggesting that CKAP4 may represent a therapeutic target for cancers expressing both DKK1 and CKAP4. This review will provide details of the novel DKK1-CKAP4 signalling axis that promotes cancer proliferation and discuss the possibility of targeting this pathway in future cancer drug development.
Linked articles: This article is part of a themed section on WNT Signalling: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v174.24/issuetoc.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures



References
-
- Aguilera O, Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Paz MF, Herranz M, Espada J et al. (2006). Epigenetic inactivation of the Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF‐1 (DKK‐1) gene in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene 25: 4116–4121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

