Inflammatory microRNA-194 and -515 attenuate the biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate during human intervertebral disc degeneration
- PMID: 28514734
- PMCID: PMC5564769
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17571
Inflammatory microRNA-194 and -515 attenuate the biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate during human intervertebral disc degeneration
Abstract
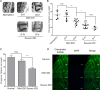
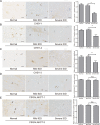
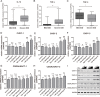
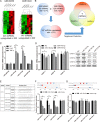
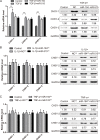
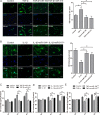
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is characterized by dehydration and loss of extracellular matrixes in the nucleus pulposus region. Chondroitin sulfate has been found to be the water-binding molecule that played a key role in IDD. Although investigators have reported that inflammatory cytokines are involved in the reduction of chondroitin sulfate in IDD, but the underlying mechanism is unrevealed. Since chondroitin sulfate synthesis is controlled by chondroitin sulfate glycosyltransferases CHSY-1/2/3 and CSGALNACT-1/2, their functional role and regulatory mechanism in IDD is not fully studied. Here, we set out to investigate the function and regulatory roles of these factors during IDD development. We found that among these chondroitin sulfate glycosyltransferases, CHSY-1/2/3 are significantly down-regulated in severe IDD samples than mild IDD samples. In vitro experiments revealed that Interleukin-1β and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α stimulation led to significant reduction of CHSY-1/2/3 at protein level than mRNA level in NP cells, indicating a post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms are involved. By computational prediction and analysis, we found that inflammatory cytokines stimulated microRNA-194 and -515 target CHSY-1/2/3 mRNA and significantly interrupt their translation and downstream chondroitin sulfate deposition. Inhibition of microRNA-194 and -515 however, significantly rescued CHSY-1/2/3 expressions and chondroitin sulfate deposition. These findings together demonstrated a vital role of inflammatory stimulated microRNAs in promoting intervertebral disc degeneration by interrupt chondroitin sulfate synthesis, which may provide new insights into the mechanism and therapeutic approaches in IDD.
Keywords: biosynthesis; chondroitin sulfate; glycosyltransferases; intervertebral disc degeneration; nucleus pulposus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Luoma K, Riihimaki H, Luukkonen R, Raininko R, Viikari-Juntura E, Lamminen A. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine. 2000;25:487–92. - PubMed
-
- Deyo RA, Weinstein JN. Low back pain. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:363–70. - PubMed
-
- Kepler CK, Ponnappan RK, Tannoury CA, Risbud MV, Anderson DG. The molecular basis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 2013;13:318–30. - PubMed
-
- Vergroesen PP, Kingma I, Emanuel KS, Hoogendoorn RJ, Welting TJ, van Royen BJ, van Dieën JH, Smit TH. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: a vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23:1057–70. - PubMed
-
- Sivan SS, Hayes AJ, Wachtel E, Caterson B, Merkher Y, Maroudas A, Brown S, Roberts S. Biochemical composition and turnover of the extracellular matrix of the normal and degenerate intervertebral disc. Eur Spine J. 2014;23:S344–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

