Electrocardiographic QRS-T angle and the risk of incident silent myocardial infarction in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study
- PMID: 28515002
- PMCID: PMC5612427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2017.05.001
Electrocardiographic QRS-T angle and the risk of incident silent myocardial infarction in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study
Abstract
Background: Silent myocardial infarction (SMI) accounts for about half of the total number of MIs, and is associated with poor prognosis as is clinically documented MI (CMI). The electrocardiographic (ECG) spatial QRS/T angle has been a strong predictor of cardiovascular outcomes. Whether spatial QRS/T angle also is predictive of SMI, and the easy-to-obtain frontal QRS/T angle will show similar association are currently unknown.
Methods: We examined the association between the spatial and frontal QRS/T angles, separately, with incident SMI among 9498 participants (mean age 54years, 57% women, and 20% African-American), who were free of cardiovascular disease at baseline (visit 1, 1987-1989) from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Incident SMI was defined as MI occurring after the baseline until visit 4 (1996-1998) without CMI. The frontal plane QRS/T angle was defined as the absolute difference between QRS axis and T axis. Values greater than the sex-specific 95th percentiles of the QRS/T angles were considered wide (abnormal).
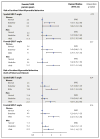
Results: A total of 317 (3.3%) incident SMIs occurred during a 9-year median follow-up. In a model adjusted for demographics, cardiovascular risk factors and potential confounders, both abnormal frontal (HR 2.28, 95% CI 1.58-3.29) and spatial (HR 2.10, 95% CI 1.44-3.06) QRS/T angles were associated with an over 2-fold increased risk of incident SMI. Similar patterns of associations were observed when the results were stratified by sex.
Conclusions: Both frontal and spatial QRS/T angles are predicative of SMI suggesting a potential use for these markers in identifying individuals at risk.
Keywords: Electrocardiography; QRS/T angle; Silent myocardial infarction.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures
Comment in
-
Electrocardiographic risk stratification of asymptomatic population without cardiovascular disease: Should we add the QRS-T angle?J Electrocardiol. 2017 Sep-Oct;50(5):543-544. doi: 10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2017.06.009. Epub 2017 Jun 8. J Electrocardiol. 2017. PMID: 28623014 No abstract available.
References
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD on behalf of the Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Redefinition of Myocardial Infarction. Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2007;116:2634–53. - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. The writing group on behalf of the Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2012;126:2020–35. - PubMed
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, et al. American Heart Association Statistics Committee; Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2016 update. A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:e255–69.
-
- Sheifer SE, Gersh BJ, Yanez ND, III, et al. Prevalence, predisposing factors, and prognosis of clinically unrecognized myocardial infarction in the elderly. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:119–26. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, Abbott RD. Incidence and prognosis of unrecognized myocardial infarction. An update on the Framingham study. Med. 1984;311:1144–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL118277/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

