Circulating soluble P-selectin must dimerize to promote inflammation and coagulation in mice
- PMID: 28515093
- PMCID: PMC5510792
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-02-770479
Circulating soluble P-selectin must dimerize to promote inflammation and coagulation in mice
Abstract
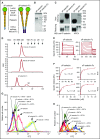
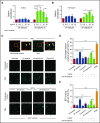
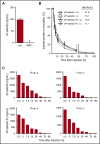
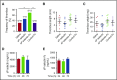
Leukocyte adhesion to P-selectin on activated platelets and endothelial cells induces shedding of the P-selectin ectodomain into the circulation. Plasma soluble P-selectin (sP-selectin) is elevated threefold to fourfold in patients with cardiovascular disease. Circulating sP-selectin is thought to trigger signaling in leukocytes that directly contributes to inflammation and thrombosis. However, sP-selectin likely circulates as a monomer, and in vitro studies suggest that sP-selectin must dimerize to induce signaling in leukocytes. To address this discrepancy, we expressed the entire ectodomain of mouse P-selectin as a monomer (sP-selectin) or as a disulfide-linked dimer fused to the Fc portion of mouse immunoglobulin G (sP-selectin-Fc). Dimeric sP-selectin-Fc, but not monomeric sP-selectin, triggered integrin-dependent adhesion of mouse leukocytes in vitro. Antibody-induced oligomerization of sP-selectin or sP-selectin-Fc was required to trigger formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. Injecting sP-selectin-Fc, but not sP-selectin, into mice augmented integrin-dependent adhesion of neutrophils in venules, generated tissue factor-bearing microparticles, shortened plasma-clotting times, and increased thrombus frequency in the inferior vena cava. Furthermore, transgenic mice that overexpressed monomeric sP-selectin did not exhibit increased inflammation or thrombosis. We conclude that elevated plasma sP-selectin is a consequence rather than a cause of cardiovascular disease.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Soluble P-selectin is the smoke, not the fire.Blood. 2017 Jul 13;130(2):101-102. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-05-786319. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28705855 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ushiyama S, Laue TM, Moore KL, Erickson HP, McEver RP. Structural and functional characterization of monomeric soluble P-selectin and comparison with membrane P-selectin. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(20):15229-15237. - PubMed
-
- Barkalow FJ, Barkalow KL, Mayadas TN. Dimerization of P-selectin in platelets and endothelial cells. Blood. 2000;96(9):3070-3077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

