Understanding determinants of unequal distribution of stillbirth in Tehran, Iran: a concentration index decomposition approach
- PMID: 28515186
- PMCID: PMC5777464
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013644
Understanding determinants of unequal distribution of stillbirth in Tehran, Iran: a concentration index decomposition approach
Abstract
Objective: The present inquiry set to determine the economic inequality in history of stillbirth and understanding determinants of unequal distribution of stillbirth in Tehran, Iran.
Methods: A population-based cross-sectional study was conducted on 5170 pregnancies in Tehran, Iran, since 2015. Principal component analysis (PCA) was applied to measure the asset-based economic status. Concentration index was used to measure socioeconomic inequality in stillbirth and then decomposed into its determinants.
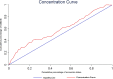
Results: The concentration index and its 95% CI for stillbirth was -0.121 (-0.235 to -0.002). Decomposition of the concentration index showed that mother's education (50%), mother's occupation (30%), economic status (26%) and father's age (12%) had the highest positive contributions to measured inequality in stillbirth history in Tehran. Mother's age (17%) had the highest negative contribution to inequality.
Conclusions: Stillbirth is unequally distributed among Iranian women and is mostly concentrated among low economic status people. Mother-related factors had the highest positive and negative contributions to inequality, highlighting specific interventions for mothers to redress inequality.
Keywords: Tehran; concentration index; decomposition; socioeconomic inequality; stillbirth.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Socioeconomic inequality of unintended pregnancy in the Iranian population: a decomposition approach.BMC Public Health. 2018 May 9;18(1):607. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5515-5. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29739402 Free PMC article.
-
Why caesarean is more unequally concentrated among better-off people in Tehran? A concentration index decomposition approach.J Epidemiol Community Health. 2019 Feb;73(2):182-187. doi: 10.1136/jech-2017-210432. Epub 2018 Nov 15. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2019. PMID: 30442819
-
Decomposition of socioeconomic inequalities in preterm deliveries in Tehran, Iran.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2018 Jan;140(1):87-92. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.12347. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2018. PMID: 29023698
-
Understanding determinants of socioeconomic inequality in mental health in Iran's capital, Tehran: a concentration index decomposition approach.Int J Equity Health. 2012 Mar 26;11:18. doi: 10.1186/1475-9276-11-18. Int J Equity Health. 2012. PMID: 22449237 Free PMC article.
-
Mother's education is the most important factor in socio-economic inequality of child stunting in Iran.Public Health Nutr. 2014 Sep;17(9):2010-5. doi: 10.1017/S1368980013002280. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Public Health Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24171933 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Measurement components of socioeconomic status in health-related studies in Iran.BMC Res Notes. 2019 Jan 31;12(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4101-y. BMC Res Notes. 2019. PMID: 30704521 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Gestational Weight Gain on Cesarean Delivery Risk, Perinatal Birth Weight and Gestational Age in Women with Normal Pre-pregnancy BMI.J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2018 Aug;68(4):258-263. doi: 10.1007/s13224-017-1023-2. Epub 2017 Jun 15. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2018. PMID: 30065539 Free PMC article.
-
Research on equity of medical resource allocation in Yangtze River Economic Belt under healthy China strategy.Front Public Health. 2023 Jun 26;11:1175276. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1175276. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37435525 Free PMC article.
-
Socioeconomic inequality of unintended pregnancy in the Iranian population: a decomposition approach.BMC Public Health. 2018 May 9;18(1):607. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5515-5. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29739402 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting socioeconomic inequality with noncommunicable diseases: Insights from a population-based survey using the concentration index in Kong cohort study.Health Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 5;6(11):e1682. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1682. eCollection 2023 Nov. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37936619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zarei S, Memari AH, Moshayedi P, et al. . Psychometric properties of physical activity and leisure motivation scale in Farsi: an international collaborative project on motivation for physical activity and leisure. Arch Iran Med 2016;19:704–10. doi:0161910/AIM.007 - PubMed
-
- World Health Organisation. The neglected tragedy of stillbirths. 2015.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical