Responses of Purkinje cells in the oculomotor vermis of monkeys during smooth pursuit eye movements and saccades: comparison with floccular complex
- PMID: 28515286
- PMCID: PMC5539460
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00209.2017
Responses of Purkinje cells in the oculomotor vermis of monkeys during smooth pursuit eye movements and saccades: comparison with floccular complex
Abstract
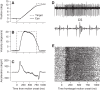
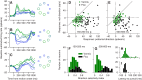
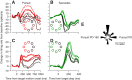
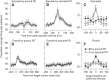
We recorded the responses of Purkinje cells in the oculomotor vermis during smooth pursuit and saccadic eye movements. Our goal was to characterize the responses in the vermis using approaches that would allow direct comparisons with responses of Purkinje cells in another cerebellar area for pursuit, the floccular complex. Simple-spike firing of vermis Purkinje cells is direction selective during both pursuit and saccades, but the preferred directions are sufficiently independent so that downstream circuits could decode signals to drive pursuit and saccades separately. Complex spikes also were direction selective during pursuit, and almost all Purkinje cells showed a peak in the probability of complex spikes during the initiation of pursuit in at least one direction. Unlike the floccular complex, the preferred directions for simple spikes and complex spikes were not opposite. The kinematics of smooth eye movement described the simple-spike responses of vermis Purkinje cells well. Sensitivities were similar to those in the floccular complex for eye position and considerably lower for eye velocity and acceleration. The kinematic relations were quite different for saccades vs. pursuit, supporting the idea that the contributions from the vermis to each kind of movement could contribute independently in downstream areas. Finally, neither the complex-spike nor the simple-spike responses of vermis Purkinje cells were appropriate to support direction learning in pursuit. Complex spikes were not triggered reliably by an instructive change in target direction; simple-spike responses showed very small amounts of learning. We conclude that the vermis plays a different role in pursuit eye movements compared with the floccular complex.NEW & NOTEWORTHY The midline oculomotor cerebellum plays a different role in smooth pursuit eye movements compared with the lateral, floccular complex and appears to be much less involved in direction learning in pursuit. The output from the oculomotor vermis during pursuit lies along a null-axis for saccades and vice versa. Thus the vermis can play independent roles in the two kinds of eye movement.
Keywords: cerebellum; complex spikes; kinematic models; motor learning; simple spikes.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Changes in the responses of Purkinje cells in the floccular complex of monkeys after motor learning in smooth pursuit eye movements.J Neurophysiol. 2000 Dec;84(6):2945-60. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.84.6.2945. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 11110823 Free PMC article.
-
Visual responses of Purkinje cells in the cerebellar flocculus during smooth-pursuit eye movements in monkeys. I. Simple spikes.J Neurophysiol. 1990 May;63(5):1241-61. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.5.1241. J Neurophysiol. 1990. PMID: 2358872
-
Purkinje cells of the cerebellar dorsal vermis: simple-spike activity during pursuit and passive whole-body rotation.J Neurophysiol. 2002 Apr;87(4):1836-49. doi: 10.1152/jn.00150.2001. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11929905
-
Role of the Vermal Cerebellum in Visually Guided Eye Movements and Visual Motion Perception.Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2019 Sep 15;5:247-268. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-091718-015000. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31299168 Review.
-
Cerebellar control of saccadic eye movements: its neural mechanisms and pathways.Jpn J Physiol. 1991;41(3):351-68. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.41.351. Jpn J Physiol. 1991. PMID: 1960885 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Kinematic Encoding of Saccades and Smooth-pursuit Eye Movements by Fastigial Neurons.Neurosci Bull. 2022 Aug;38(8):927-932. doi: 10.1007/s12264-022-00857-2. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Neurosci Bull. 2022. PMID: 35486343 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Encoding of error and learning to correct that error by the Purkinje cells of the cerebellum.Nat Neurosci. 2018 May;21(5):736-743. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0136-y. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Nat Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29662213 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebellar circuit computations for predictive motor control.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2025 Sep;26(9):538-553. doi: 10.1038/s41583-025-00936-z. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40523942 Review.
-
Complex Spike Wars: a New Hope.Cerebellum. 2018 Dec;17(6):735-746. doi: 10.1007/s12311-018-0960-3. Cerebellum. 2018. PMID: 29982917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebellar projections to the macaque midbrain tegmentum: Possible near response connections.Vis Neurosci. 2021 May 12;38:E007. doi: 10.1017/S0952523821000067. Vis Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33977889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berens P. CircStat: a MATLAB toolbox for circular statistics. J Stat Softw 31: 1–21, 2009. doi:10.18637/jss.v031.i10. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

