Early Onset of Nucleate Boiling on Gas-covered Biphilic Surfaces
- PMID: 28515431
- PMCID: PMC5435692
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02163-8
Early Onset of Nucleate Boiling on Gas-covered Biphilic Surfaces
Abstract
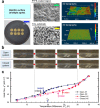
For phase-change cooling schemes for electronics, quick activation of nucleate boiling helps safeguard the electronics components from thermal shocks associated with undesired surface superheating at boiling incipience, which is of great importance to the long-term system stability and reliability. Previous experimental studies show that bubble nucleation can occur surprisingly early on mixed-wettability surfaces. In this paper, we report unambiguous evidence that such unusual bubble generation at extremely low temperatures-even below the boiling point-is induced by a significant presence of incondensable gas retained by the hydrophobic surface, which exhibits exceptional stability even surviving extensive boiling deaeration. By means of high-speed imaging, it is revealed that the consequently gassy boiling leads to unique bubble behaviour that stands in sharp contrast with that of pure vapour bubbles. Such findings agree qualitatively well with numerical simulations based on a diffuse-interface method. Moreover, the simulations further demonstrate strong thermocapillary flows accompanying growing bubbles with considerable gas contents, which is associated with heat transfer enhancement on the biphilic surface in the low-superheat region.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Single-bubble dynamics in pool boiling of one-component fluids.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2014 Jun;89(6):063002. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.89.063002. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2014. PMID: 25019874
-
Large-scale Generation of Patterned Bubble Arrays on Printed Bi-functional Boiling Surfaces.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 1;6:23760. doi: 10.1038/srep23760. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27034255 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Surface Wettability on Bubble Formation and Motion.Langmuir. 2021 Dec 14;37(49):14483-14490. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c02444. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Langmuir. 2021. PMID: 34851638
-
Enhancing Liquid-Vapor Phase-Change Heat Transfer with Micro/Nano-Structured Surfaces.ACS Nano. 2025 Mar 18;19(10):9513-9589. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c15277. Epub 2025 Mar 10. ACS Nano. 2025. PMID: 40062720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Innovative Surface-Modification Routes for Pool Boiling Enhancement.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Feb 22;15(3):302. doi: 10.3390/mi15030302. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38542549 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Sub-Nanoscale Surface Topography on Contact Line Profile: Insights from Coherence Scanning Interferometry.Langmuir. 2025 Jan 14;41(1):917-925. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c04227. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Langmuir. 2025. PMID: 39719270 Free PMC article.
-
Laser-Engineered Microcavity Surfaces with a Nanoscale Superhydrophobic Coating for Extreme Boiling Performance.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 May 27;12(21):24419-24431. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c01594. Epub 2020 May 12. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32352743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gerardi C, Buongiorno J, Hu L-W, McKrell T. Study of bubble growth in water pool boiling through synchronized, infrared thermometry and high-speed video. Int. J. Heat and Mass Tran. 2010;53:4185–4192. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2010.05.041. - DOI
-
- O’Hanley H, et al. Separate effects of surface roughness, wettability, and porosity on the boiling critical heat flux. App. Phy. Lett. 2013;103:024102. doi: 10.1063/1.4813450. - DOI
-
- Mudawar I. Assessment of high-heat-flux thermal management schemes. IEEE T. Compon. Pack. T. 2001;24:122–141. doi: 10.1109/6144.926375. - DOI
-
- Attinger D, et al. Surface engineering for phase change heat transfer: a review. MRS Energy & Sustainability. 2014;1:1–40. doi: 10.1557/mre.2014.9. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

