Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 28515434
- PMCID: PMC5759779
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn.2017.48
Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
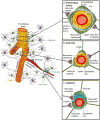
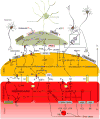
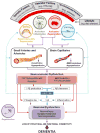
Cerebral blood flow (CBF) regulation is essential for normal brain function. The mammalian brain has evolved a unique mechanism for CBF control known as neurovascular coupling. This mechanism ensures a rapid increase in the rate of CBF and oxygen delivery to activated brain structures. The neurovascular unit is composed of astrocytes, mural vascular smooth muscle cells and pericytes, and endothelia, and regulates neurovascular coupling. This Review article examines the cellular and molecular mechanisms within the neurovascular unit that contribute to CBF control, and neurovascular dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer disease.
Figures

References
-
- Iadecola C. Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:347–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

