Protein kinase C inhibitor chelerythrine selectively inhibits proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer cells
- PMID: 28515445
- PMCID: PMC5435721
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02222-0
Protein kinase C inhibitor chelerythrine selectively inhibits proliferation of triple-negative breast cancer cells
Abstract
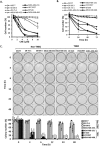
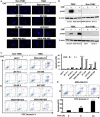
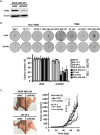
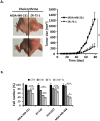
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a subtype of breast cancer lacking targeted therapy currently. Recent studies imply that protein kinase C may play important roles in TNBC development and could be a specific target. In this study, we evaluated the anti-proliferative activity of PKC inhibitor chelerythrine on a panel of breast cancer cell lines. Chelerythrine selectively inhibited the growth of TNBC cell lines compared to non-TNBC cell lines as demonstrated by in vitro cell proliferation assay and colony formation assay, as well as evidenced by in vivo xenograft assay. The selective anti-proliferative effect of chelerythrine was associated with induction of apoptosis in TNBC cell lines. We further demonstrated that PKN2, one of the PKC subtypes, was highly expressed in TNBC cell lines, and knocking down PKN2 in TNBC cells inhibited colony formation and xenograft growth. This indicates that PKN2 is required for the survival of TNBC cells, and could be the target mediates the selective activity of chelerythrine. Finally, combination of chelerythrine and chemotherapy reagent taxol showed synergistic/additive effect on TNBC cell lines. Our results suggest chelerythrine or other PKC inhibitors may be promising regimens for TNBC tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- IARC, W. GLOBOCAN: Estimated Cancer Incidence, Mortality, and Prevalence Worldwide in 2012 (IARC, 2014).
-
- Brenton JD, Carey LA, Ahmed AA, Caldas C. Molecular classification and molecular forecasting of breast cancer: ready for clinical application? Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23:7350–7360. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.03.3845. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

