Comparison of Airtraq™, McCoy™ and Macintosh laryngoscopes for endotracheal intubation in patients with cervical spine immobilisation: A randomised clinical trial
- PMID: 28515522
- PMCID: PMC5416724
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_517_16
Comparison of Airtraq™, McCoy™ and Macintosh laryngoscopes for endotracheal intubation in patients with cervical spine immobilisation: A randomised clinical trial
Abstract
Background and aims: The study aimed at comparing the performance of the novel optical Airtraq™ laryngoscope with the McCoy™ and conventional Macintosh laryngoscopes for ease of endotracheal intubation in patients with neck immobilisation using manual inline axial cervical spine stabilisation (MIAS) technique.
Methods: Ninety consenting American Society of Anaesthesiologist's physical status I-II patients, aged 18-60 years, scheduled for various surgeries requiring tracheal intubation were randomly assigned into three groups of thirty each to undergo intubation with Macintosh, Airtraq™, or McCoy™ laryngoscope with neck immobilisation by MIAS technique. The ease of intubation based on Intubation difficulty scale (IDS) score, Cormack-Lehane grade of glottic view, optimisation manoeuvres and impact on haemodynamic parameters were recorded. Statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA and Bonferroni correction for post hoc tests.
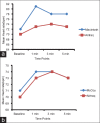
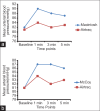
Results: All patients in three groups had a comparable demographic profile and were successfully intubated. The Airtraq™ laryngoscope significantly reduced the IDS (mean - 0.43 ± 0.81) as compared with both McCoy™ (mean - 1.63 ± 1.49, P = 0.001) and Macintosh laryngoscope (mean -2.23 ± 1.92, P < 0.001) and improved the Cormack-Lehane glottic view (77% grade 1 view and no patients with grade 3 or 4 view). There were less haemodynamic variations during laryngoscopy with the Airtraq™ compared to the Macintosh laryngoscope, but there was not between the Airtraq™ and McCoy™ laryngoscope groups.
Conclusion: In patients undergoing endotracheal intubation with cervical immobilisation, Airtraq™ laryngoscope was superior to the McCoy™ and Macintosh laryngoscopes, with greater ease of intubation and lower impact on haemodynamic variables.
Keywords: Airtraq™; Macintosh laryngoscope; McCoy™; airway management; cervical immobilisation.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peterson GN, Domino KB, Caplan RA, Posner KL, Lee LA, Cheney FW. Management of the difficult airway: A closed claims analysis. Anesthesiology. 2005;103:33–9. - PubMed
-
- Maharaj CH, O'Croinin D, Curley G, Harte BH, Laffey JG. A comparison of tracheal intubation using the Airtraq or the Macintosh laryngoscope in routine airway management: A randomised, controlled clinical trial. Anaesthesia. 2006;61:1093–9. - PubMed
-
- Tolon MA, Zanty OM, Shafshak W, Arida EE. Comparative study between the use of Macintosh laryngoscope and Airtraq in patients with cervical spine immobilisation. Alex J Med. 2012;48:179–85.
-
- McCoy EP, Mirakhur RK. The levering laryngoscope. Anaesthesia. 1993;48:516–9. - PubMed
-
- Uchida T, Hikawa Y, Saito Y, Yasuda K. The McCoy™ levering laryngoscope in patients with limited neck extension. Can J Anaesth. 1997;44:674–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

