Infectious pneumonia in the immunocompetent host: What the radiologist should know
- PMID: 28515580
- PMCID: PMC5385769
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-3026.202967
Infectious pneumonia in the immunocompetent host: What the radiologist should know
Abstract
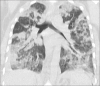
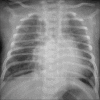
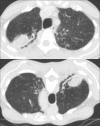
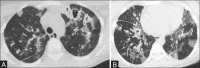
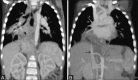
Lung infections are an important cause of morbidity and mortality, particularly because of the rising antimicrobial resistance. According to the clinical setting, they can be categorized as community-acquired pneumonia and hospital-acquired pneumonia. Radiological patterns of lung infections are lobar consolidation, bronchopneumonia, interstitial pattern, and nodular pattern. In addition, typical imaging features of several infections serve as "red flag signs" in reaching a diagnosis or altering the management. It would be prudent for the radiologist to be well informed regarding these aspects of lung infections to be able to make a valuable contribution to the management.
Keywords: Imaging; immunocompetent; lung infections; pneumonia; radiological signs.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Imaging in pulmonary infections of immunocompetent adult patients.Breathe (Sheff). 2024 Mar;20(1):230186. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0186-2023. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Breathe (Sheff). 2024. PMID: 38595938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiologic predictors of hyponatremia in children hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia.Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012 Aug;28(8):764-6. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e3182624b98. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012. PMID: 22858749
-
Imaging of bacterial pulmonary infection in the immunocompetent patient.Semin Roentgenol. 2007 Apr;42(2):122-45. doi: 10.1053/j.ro.2006.08.008. Semin Roentgenol. 2007. PMID: 17394925 Review.
-
Pneumococcal pneumonia in patients requiring hospitalization: effects of bacteremia and HIV seropositivity on radiographic appearance.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000 Dec;175(6):1533-6. doi: 10.2214/ajr.175.6.1751533. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. PMID: 11090369
-
[Relation between clinical-biological aspects and CD4 lymphocyte count in HIV/AIDS patients with non-tuberculous bronchopulmonary infection].Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2012 Apr-Jun;116(2):457-63. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2012. PMID: 23077937 Romanian.
References
-
- Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Hospital-acquired, Ventilator-associated, and Healthcare-associated Pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:388–416. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

