A complete tool set for molecular QTL discovery and analysis
- PMID: 28516912
- PMCID: PMC5454369
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15452
A complete tool set for molecular QTL discovery and analysis
Abstract
Population scale studies combining genetic information with molecular phenotypes (for example, gene expression) have become a standard to dissect the effects of genetic variants onto organismal phenotypes. These kinds of data sets require powerful, fast and versatile methods able to discover molecular Quantitative Trait Loci (molQTL). Here we propose such a solution, QTLtools, a modular framework that contains multiple new and well-established methods to prepare the data, to discover proximal and distal molQTLs and, finally, to integrate them with GWAS variants and functional annotations of the genome. We demonstrate its utility by performing a complete expression QTL study in a few easy-to-perform steps. QTLtools is open source and available at https://qtltools.github.io/qtltools/.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
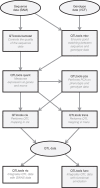
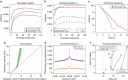
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

