Cycloheximide promotes paraptosis induced by inhibition of cyclophilins in glioblastoma multiforme
- PMID: 28518150
- PMCID: PMC5520731
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.217
Cycloheximide promotes paraptosis induced by inhibition of cyclophilins in glioblastoma multiforme
Abstract
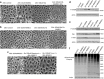
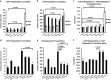
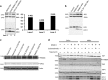
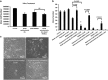
Cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide. Current treatment strategies based on multi-agent chemotherapy and/or radiation regimens have improved overall survival in some cases. However, resistance to apoptosis often develops in cancer cells, and its occurrence is thought to contribute to treatment failure. Non-apoptotic cell death mechanisms have become of great interest, therefore, in hopes that they would bypass tumor cell resistance. Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), a grade IV astrocytic tumor is the most frequent brain tumor in adults, and has a high rate of mortality. We report that NIM811, a small molecule cyclophilin-binding inhibitor, induces catastrophic vacuolization and cell death in GBM cells. These unique features are distinct from many known cell death pathways, and are associated with an incompletely defined cell death mechanism known as paraptosis. We found that NIM811-induced paraptosis is due to unresolved ER stress. The abnormal upregulation of protein translation was responsible for the build-up of misfolded or unfolded proteins in ER, whereas pro-survival autophagy and UPR signals were shutdown during prolonged treatment with NIM811. Although cycloheximide has been claimed to suppress paraptosis, instead we find that it only temporarily delayed vacuole formation, but actually enhanced paraptotic cell death in the long term. On the other hand, mTOR inhibitors rescued cells from NIM811-induced paraptosis by sustaining autophagy and the UPR, while specifically restraining cap-dependent translation. These findings not only provide new insights into the mechanisms underlying paraptosis, but also shed light on a potential approach to enhance GBM treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Paraptosis accompanied by autophagy and apoptosis was induced by celastrol, a natural compound with influence on proteasome, ER stress and Hsp90.J Cell Physiol. 2012 May;227(5):2196-206. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22956. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 21866552
-
Honokiol induces paraptosis-like cell death of acute promyelocytic leukemia via mTOR & MAPK signaling pathways activation.Apoptosis. 2021 Apr;26(3-4):195-208. doi: 10.1007/s10495-020-01655-9. Epub 2021 Feb 7. Apoptosis. 2021. PMID: 33550458 Free PMC article.
-
Protein synthesis inhibition enhances paraptotic death induced by inhibition of cyclophilins in glioblastoma cells.Cancer Cell Microenviron. 2017;4(3):e1601. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Cancer Cell Microenviron. 2017. PMID: 29085850 Free PMC article.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum stress/unfolded protein response in gliomagenesis, tumor progression and as a therapeutic target in glioblastoma.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Oct 15;118:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.04.008. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27106078 Review.
-
Small-molecule compounds target paraptosis to improve cancer therapy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Oct;118:109203. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109203. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31306970 Review.
Cited by
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells as a novel cancer vaccine.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019 Nov;19(11):1191-1197. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2019.1650909. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31364894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Purified Resin Glycoside Fraction from Pharbitidis Semen Induces Paraptosis by Activating Chloride Intracellular Channel-1 in Human Colon Cancer Cells.Integr Cancer Ther. 2019 Jan-Dec;18:1534735418822120. doi: 10.1177/1534735418822120. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Integr Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 30614302 Free PMC article.
-
The thiosemicarbazone Me2NNMe2 induces paraptosis by disrupting the ER thiol redox homeostasis based on protein disulfide isomerase inhibition.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Oct 15;9(11):1052. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1102-z. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30323190 Free PMC article.
-
The Multiple Roles of Peptidyl Prolyl Isomerases in Brain Cancer.Biomolecules. 2018 Oct 11;8(4):112. doi: 10.3390/biom8040112. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30314361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptosis, Paraptosis and Autophagy: Death and Survival Pathways Associated with Photodynamic Therapy.Photochem Photobiol. 2019 Jan;95(1):119-125. doi: 10.1111/php.12952. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Photochem Photobiol. 2019. PMID: 29882356 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ellor SV, Pagano-Young TA, Avgeropoulos NG. Glioblastoma: background, standard treatment paradigms, and supportive care considerations. J Law Med Ethics 2014; 42: 171–182. - PubMed
-
- Lee D, Kim IY, Saha S, Choi KS. Paraptosis in the anti-cancer arsenal of natural products. Pharmacol Ther 2016; 162: 120–133. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

