Aging and Parkinson's disease: Different sides of the same coin?
- PMID: 28520211
- PMCID: PMC5844262
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.27037
Aging and Parkinson's disease: Different sides of the same coin?
Abstract
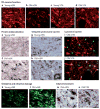
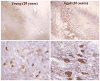
Despite abundant epidemiological evidence in support of aging as the primary risk factor for PD, biological correlates of a connection have been elusive. In this article, we address the following question: does aging represent biology accurately characterized as pre-PD? We present evidence from our work on midbrain dopamine neurons of aging nonhuman primates that demonstrates that markers of known correlates of dopamine neuron degeneration in PD, including impaired proteasome/lysosome function, oxidative/nitrative damage, and inflammation, all increase with advancing age and are exaggerated in the ventral tier substantia nigra dopamine neurons most vulnerable to degeneration in PD. Our findings support the view that aging-related changes in the dopamine system approach the biological threshold for parkinsonism, actively producing a vulnerable pre-parkinsonian state. © 2017 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; aging; lysosome; microglia; nonhuman primates; oxidative stress; proteasome.
© 2017 The Authors. Movement Disorders published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bennett DA, Beckett LA, Murray AM, et al. Prevalence of parkin-sonian signs and associated mortality in a community population of older people. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:71–76. - PubMed
-
- Calne DB, Langston JW. Aetiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 1983;2:1457–1479. - PubMed
-
- Sulzer D. Multiple hit hypothesis for dopamine neuron loss in Parkinson’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 2007;30:244–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

