Development of a written assessment for a national interprofessional cardiotocography education program
- PMID: 28521768
- PMCID: PMC5437628
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-017-0915-2
Development of a written assessment for a national interprofessional cardiotocography education program
Abstract
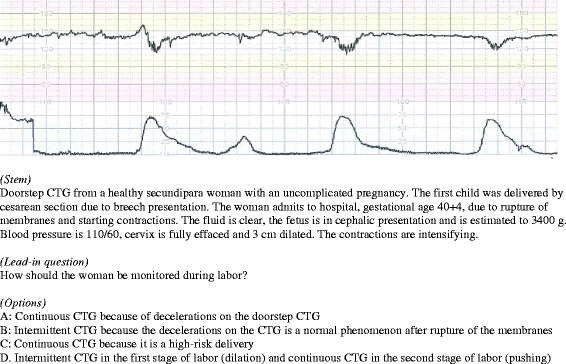
Background: To reduce the incidence of hypoxic brain injuries among newborns a national cardiotocography (CTG) education program was implemented in Denmark. A multiple-choice question test was integrated as part of the program. The aim of this article was to describe and discuss the test development process and to introduce a feasible method for written test development in general.
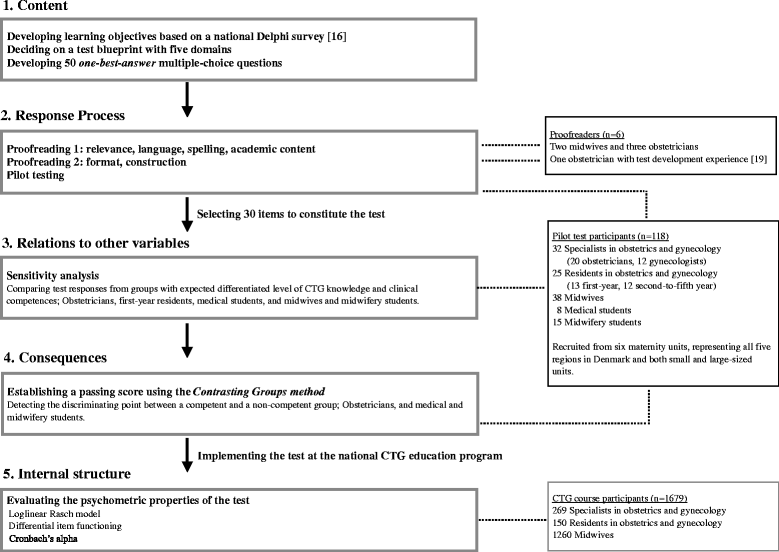
Methods: The test development was based on the unitary approach to validity. The process involved national consensus on learning objectives, standardized item writing, pilot testing, sensitivity analyses, standard setting and evaluation of psychometric properties using Item Response Theory models. Test responses and feedback from midwives, specialists and residents in obstetrics and gynecology, and medical and midwifery students were used in the process (proofreaders n = 6, pilot test participants n = 118, CTG course participants n = 1679).
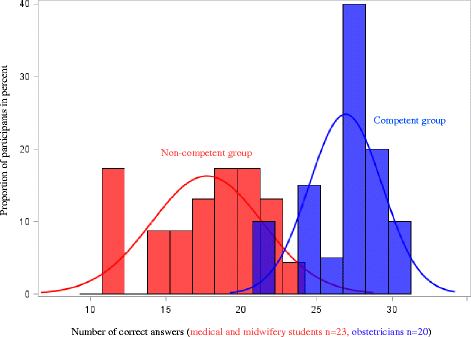
Results: The final test included 30 items and the passing score was established at 25 correct answers. All items fitted a loglinear Rasch model and the test was able to discriminate levels of competence. Seven items revealed differential item functioning in relation to profession and geographical regions, which means the test is not suitable for measuring differences between midwives and physicians or differences across regions. In the setting of pilot testing Cronbach's alpha equaled 0.79, whereas Cronbach's alpha equaled 0.63 in the setting of the CTG education program. This indicates a need for more items and items with a higher degree of difficulty in the test, and illuminates the importance of context when discussing validity.
Conclusions: Test development is a complex and time-consuming process. The unitary approach to validity was a useful and applicable tool for development of a CTG written assessment. The process and findings supported our proposed interpretation of the assessment as measuring CTG knowledge and interpretive skills. However, for the test to function as a high-stake assessment a higher reliability is required.
Keywords: Cardiotocography; Continuing professional development; Fetal monitoring; Interprofessional; Multiple-choice question; Validity; Written assessment.
Figures
References
-
- Sentinel event alert, Issue 30 (2004): Preventing infant death and injury during delivery. Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations. http://www.jointcommission.org/assets/1/18/sea_30.pdf.
-
- Sikre fødsler [Safe Deliveries]. http://www.dsog.dk/wp/dsog/projekt-sikre-fodsler.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources