B cell repopulation kinetics after rituximab treatment in ANCA-associated vasculitides compared to rheumatoid arthritis, and connective tissue diseases: a longitudinal observational study on 120 patients
- PMID: 28521808
- PMCID: PMC5437549
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-017-1306-0
B cell repopulation kinetics after rituximab treatment in ANCA-associated vasculitides compared to rheumatoid arthritis, and connective tissue diseases: a longitudinal observational study on 120 patients
Abstract
Background: B cell depletion with rituximab (RTX) is approved for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and ANCA-associated vasculitides (AAV). Recently, RTX has been shown to be effective in AAV maintenance therapy, but an optimal RTX treatment schedule is unknown and the time to B cell repopulation after RTX has not been studied.
Methods: Retrospective single-center analysis of B cell repopulation in patients with AAV, RA or connective tissue disease (CTD) treated with RTX.
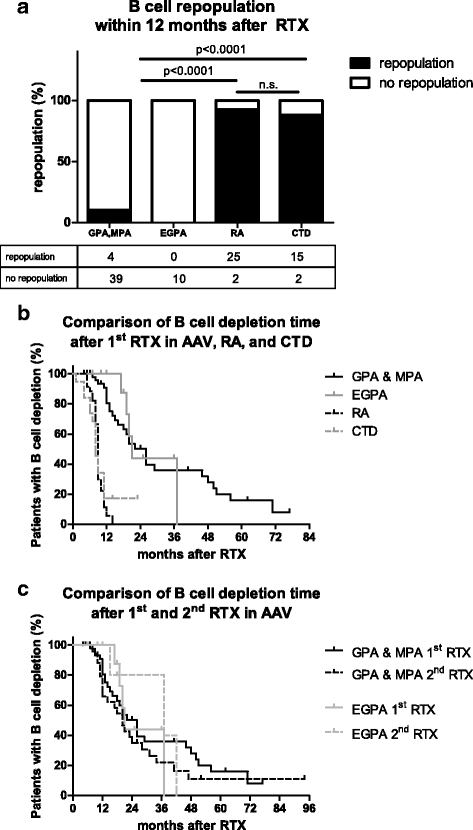
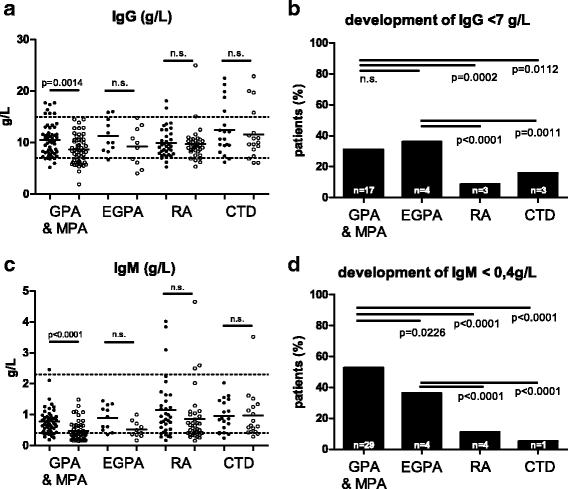
Results: Beginning B cell repopulation within the first year after RTX treatment was observed in 93% of RA and 88% of CTD patients. Only 10% of patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) and no patient with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) showed B cell repopulation within this time. Median time of B cell depletion was 26 months in GPA/MPA, and 21 months in EGPA compared to 9 months in RA, and 8 months in CTD (p < 0.0001). In 25 AAV-patients B cell depletion lasted for at least 44 months. There was a significant decline in serum immunoglobulin concentrations in GPA/MPA patients, but not in patients with RA or CTD. Significantly more GPA/MPA patients developed hygogammaglobulinemia (IgG <7 g/L) compared to patients with RA or CTD.
Conclusions: In contrast to RA and CTD, in AAV RTX induces long-lasting depletion of B cells that is associated with decreased antibody production. This observation points toward potential defects in the B cell compartment in AAV that are unmasked by immunosuppressive treatment and has important implications for the design of maintenance treatment schedules using RTX.
Keywords: ANCA; B lymphocyte; Hypogammaglobulinemia; Repopulation; Rituximab.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reconstitution of the peripheral B lymphocyte compartment in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides treated with rituximab for relapsing or refractory disease.Autoimmunity. 2014 Sep;47(6):401-8. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2014.914174. Epub 2014 May 6. Autoimmunity. 2014. PMID: 24798501
-
Rituximab-associated hypogammaglobulinemia in autoimmune rheumatic diseases: a single-center retrospective cohort study.Rheumatol Int. 2021 Jun;41(6):1115-1124. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04847-x. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Rheumatol Int. 2021. PMID: 33811499 Free PMC article.
-
Rituximab as Induction Therapy in Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Refractory to Conventional Immunosuppressive Treatment: A 36-Month Follow-Up Analysis.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017 Nov-Dec;5(6):1556-1563. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2017.07.027. Epub 2017 Sep 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017. PMID: 28916432
-
B-cell-targeted therapy in systemic vasculitis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016 Jan;28(1):15-20. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000235. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26599379 Review.
-
Rituximab in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017 Feb;19(2):6. doi: 10.1007/s11926-017-0632-1. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28155022 Review.
Cited by
-
A Patient with Cryoglobulinemic Membranoproliferative GN (MPGN) Who Survived COVID-19 Disease: Case Presentation and Current Data of COVID-19 Infection in Dialysis and Transplanted Patients in Greece.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Jul 17;56(7):355. doi: 10.3390/medicina56070355. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32708858 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting FcRn for immunomodulation: Benefits, risks, and practical considerations.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Sep;146(3):479-491.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.016. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32896308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictors of Immunogenic Response to the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Rituximab.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jun 6;10(6):901. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10060901. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746508 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic role of anti-nuclear autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis: Insights from other rheumatic diseases.Immunol Rev. 2024 Nov;328(1):265-282. doi: 10.1111/imr.13390. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39248128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Persistent B Cell Depletion After Rituximab for Autoimmune and Glomerular Diseases: A Case Series.Kidney Int Rep. 2025 Feb 7;10(5):1441-1449. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.02.002. eCollection 2025 May. Kidney Int Rep. 2025. PMID: 40485690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Popa C, Leandro MJ, Cambridge G, Edwards JCW. Repeated B lymphocyte depletion with rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis over 7 yrs Rheumatology. 2007;46(4):626–30. - PubMed
-
- Holle JU, Dubrau C, Herlyn K, Heller M, Ambrosch P, Noelle B, et al. Rituximab for refractory granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's granulomatosis): comparison of efficacy in granulomatous versus vasculitic manifestations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(3):327–33. doi: 10.1136/ard.2011.153601. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

