Radiotherapy improves serum fatty acids and lipid profile in breast cancer
- PMID: 28521812
- PMCID: PMC5437547
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0481-y
Radiotherapy improves serum fatty acids and lipid profile in breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is a disease with diverse clinical symptoms, molecular profiles, and its nature to response its therapeutic treatments. Radiotherapy (RT), along with surgery and chemotherapy is a part of treatment in breast cancer. The aim of present study was to investigate pre and post treatment effects of radiotherapy in serum fatty acids and its lipids profile in patients with breast cancer.
Methods: In this comparative as well as follow up study, Serum fatty acids were performed by gas chromatography to investigate fatty acids and Microlab for analysis of lipid profile.
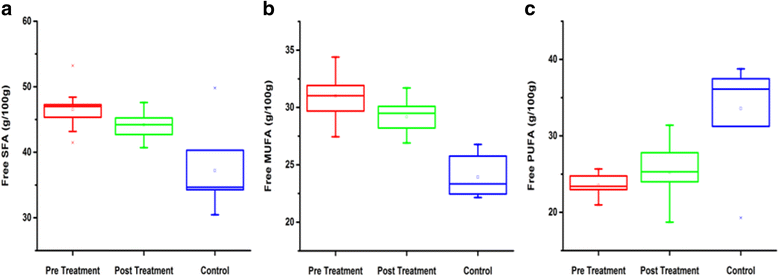
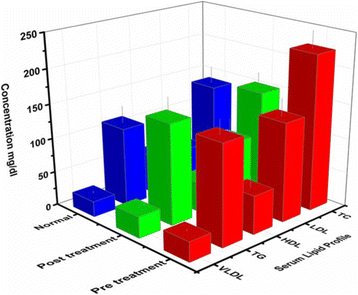
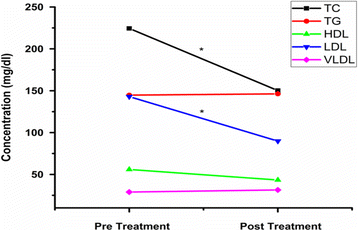
Results: Among serum free and total fatty acids the major saturated fatty acids (SFAs) in serum lipids of breast cancer patients (pre and post treated) were stearic acid (18:0) and palmitic acid (16:0). These fatty acids contributed about 35-50% of total fatty acids. The decreased concentrations of linoleic acid (C18:2) and arachidonic acid (C20:4) with a lower ratio of C18:2/C18:1 was found in pretreated breast cancer patients as compared to controls. The n-3/n-6 ratio of breast cancer patients was decreased before treatment but it was 35% increased after treatment. In addition, plasma activity of D6 desaturase was increased in the breast cancer patients, while the activity of D5 desaturase was decreased. Increased levels of SFAs, monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and decreased polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) levels in breast cancer patients (pre and post treated) as compared to controls. Serum total cholesterol (TC) (224.4 mg/dL) and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (142.9 mg/dL) were significantly increased in pretreated breast cancer patients but after the radiotherapy treatment, the TC (150.2 mg/dL) and LDL-C (89.8 mg/dL) were decreased.
Conclusion: It seems that RT would have played a potential role in the treatment of BC. After RT the serum levels of PUFAs, TC, and LDL-C are improved. Our study reinforces the important role of RT in the management of BC. The level of PUFAs, TC, and LDL-C can be used as the biomarkers for early diagnosis in individuals with risk of breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Fatty acids; Gas chromatography; Lipids; Radiotherapy.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

