Pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase or genetic deletion reduces diclofenac-induced gastric ulcers
- PMID: 28522175
- PMCID: PMC5659729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.05.018
Pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase or genetic deletion reduces diclofenac-induced gastric ulcers
Abstract
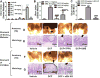
Aims: This research was conducted to evaluate the hypothesis that gastric ulcers caused by the NSAID diclofenac sodium (DCF) can be prevented by the soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor TPPU.
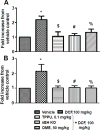
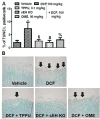
Main methods: Mice were administered a single dose of 10, 30 or 100mg/kg of DCF. Once an ulcerative dose of DCF was chosen, mice were pretreated with TPPU for 7days at 0.1mg/kg to evaluate anti-ulcer effects of the sEH inhibitor on anatomy, histopathology, pH, inflammatory markers and epithelial apoptosis of stomachs.
Key findings: Diclofenac caused ulceration of the stomach at a dose of 100mg/kg and a time post dose of 6h. Ulcers generated under these conditions were associated with a significant increase in the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in serum and increased apoptosis compared to control mice. Pretreatment with TPPU resulted in a decrease of ulceration in mice treated with DCF with a significant decrease in the level of apoptosis, TNF-α and IL-6 in the serum in comparison to diclofenac-treated mice. TPPU did not affect the pH of the stomach, whereas omeprazole elevated the pH of the stomach as expected. A similar anti-ulcer effect was observed in sEH gene knockout mice treated with DCF.
Significance: The sEH inhibitor TPPU decreases the NSAID-induced stomach ulcers.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Diclofenac; IL-6; Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor TPPU; Stomach ulcer; TNF-α.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The University of California holds numerous patents on the use of sEH inhibitors for the management of pain and inflammation. Dr. Bruce D. Hammock and Dr. Bora Inceoglu founded a company for the advancing research on the use of sEH inhibitors in companion animals and humans.
Figures

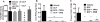
Similar articles
-
Anti-Ulcer Efficacy of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor TPPU on Diclofenac-Induced Intestinal Ulcers.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016 Jun;357(3):529-36. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.232108. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016. PMID: 26989141 Free PMC article.
-
Omeprazole increases the efficacy of a soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor in a PGE₂ induced pain model.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Dec 15;289(3):419-27. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.10.018. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26522832 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition Attenuates MPTP-Induced Neurotoxicity in the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic System: Involvement of α-Synuclein Aggregation and ER Stress.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jan;55(1):138-144. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0726-9. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28822080
-
Target-Mediated Drug Disposition-A Class Effect of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors.J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Apr;61(4):531-537. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1763. Epub 2020 Oct 19. J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33078430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Critical Review of Morphologic Findings and Data From 14 Toxicological Studies Involving Fish Exposures to Diclofenac.Toxicol Pathol. 2021 Jul;49(5):1024-1041. doi: 10.1177/0192623321989653. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Toxicol Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33596776 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of chemotherapy-induced cytokine/lipid mediator surge and ovarian cancer by a dual COX-2/sEH inhibitor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jan 29;116(5):1698-1703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803999116. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30647111 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Specific Differences in Resolution of Airway Inflammation in Fat-1 Transgenic Mice Following Repetitive Agricultural Dust Exposure.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 13;12:785193. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.785193. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35095496 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidative Action of Alpha-Linolenic Acid during Its Gastroprotective Effect in an Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Injury Model.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2025 Apr 30;30(2):132-140. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2025.30.2.132. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40352293 Free PMC article.
-
Epoxy-Oxylipins and Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Metabolic Pathway as Targets for NSAID-Induced Gastroenteropathy and Inflammation-Associated Carcinogenesis.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jun 25;10:731. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00731. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31293429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolution of eicosanoid/cytokine storm prevents carcinogen and inflammation-initiated hepatocellular cancer progression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Sep 1;117(35):21576-21587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2007412117. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32801214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laine L. Approaches to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use in the high-risk patient. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:594–606. - PubMed
-
- Singh G. Gastrointestinal complications of prescription and over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a view from the ARAMIS database. Arthritis, Rheumatism, and Aging Medical Information System. Am J Ther. 2000;7:115–121. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

