Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, Progress, and Possibilities
- PMID: 28522654
- PMCID: PMC5718284
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.11491116
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, Progress, and Possibilities
Abstract
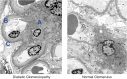
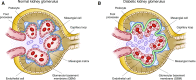
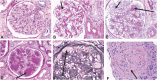
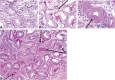
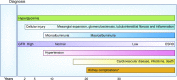
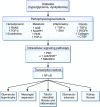
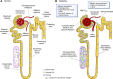
Diabetic kidney disease develops in approximately 40% of patients who are diabetic and is the leading cause of CKD worldwide. Although ESRD may be the most recognizable consequence of diabetic kidney disease, the majority of patients actually die from cardiovascular diseases and infections before needing kidney replacement therapy. The natural history of diabetic kidney disease includes glomerular hyperfiltration, progressive albuminuria, declining GFR, and ultimately, ESRD. Metabolic changes associated with diabetes lead to glomerular hypertrophy, glomerulosclerosis, and tubulointerstitial inflammation and fibrosis. Despite current therapies, there is large residual risk of diabetic kidney disease onset and progression. Therefore, widespread innovation is urgently needed to improve health outcomes for patients with diabetic kidney disease. Achieving this goal will require characterization of new biomarkers, designing clinical trials that evaluate clinically pertinent end points, and development of therapeutic agents targeting kidney-specific disease mechanisms (e.g., glomerular hyperfiltration, inflammation, and fibrosis). Additionally, greater attention to dissemination and implementation of best practices is needed in both clinical and community settings.
Keywords: altered renal hemodynamics; diabetic nephropathy; diagnosis; natural history; novel therapies; pathogenesis; structural changes.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Cameron JS: The discovery of diabetic nephropathy: From small print to centre stage. J Nephrol 19[Suppl 10]: S75–S87, 2006 - PubMed
-
- USRDS: United States Renal Data System Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2015
-
- Reutens AT: Epidemiology of diabetic kidney disease. Med Clin North Am 97: 1–18, 2013 - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization: Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases, Geneva, Switzerland, World Health Organization, 2014
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

