Selection and characterization of a DNA aptamer inhibiting coagulation factor XIa
- PMID: 28522812
- PMCID: PMC5437010
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02055-x
Selection and characterization of a DNA aptamer inhibiting coagulation factor XIa
Abstract
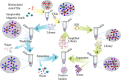
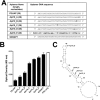
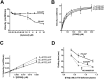
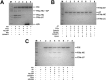
Factor XIa (FXIa) is a serine protease that catalyzes the activation of Factor IX (FIX) in the blood coagulation cascade. FXIa and its precursor FXI are emergent therapeutic targets for the development of safer anticoagulant agents. Here, we sought a novel DNA-based agent to inhibit FXIa. Towards this goal, an 80 base, single-stranded DNA aptamer library (containing a 40 base randomized core) was screened for FXIa-binding candidates, using ten rounds of positive and negative selection. After selection, 6 of 89 different sequences inhibited FXIa-mediated chromogenic substrate S2366 cleavage. The most active anti-FXIa aptamer had a hypervariable central sequence 5'-AACCTATCGGACTATTGTTAGTGATTTTTATAGTGT-3' and was designated Factor ELeven Inhibitory APtamer (FELIAP). FELIAP, but not a scrambled aptamer control (SCRAPT), competitively inhibited FXIa-catalyzed S2366 cleavage, FIX activation, and complex formation with antithrombin. No effect of FELIAP on FXI activation was observed. FELIAP inhibited plasma clotting and thrombin generation assays to a significantly greater extent than SCRAPT. Immobilized FELIAP bound FXIa with strong affinity and an equilibrium binding constant (KD) in the low nanomolar range determined using surface plasmon resonance. FELIAP is the first FXIa-inhibitory aptamer to be described and constitutes a lead compound to develop related aptamers for in vivo use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Generation and characterization of aptamers targeting factor XIa.Thromb Res. 2017 Aug;156:134-141. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2017.06.015. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Thromb Res. 2017. PMID: 28644959 Free PMC article.
-
Binding-Site Directed Selection and Large-Scale Click-Synthesis of a Coagulation Factor XIa-Inhibiting Circular DNA Aptamer.Chemistry. 2025 Mar 17;31(16):e202404372. doi: 10.1002/chem.202404372. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Chemistry. 2025. PMID: 39822082
-
Development of an Ultrasensitive Competitive Double-Enzyme Cascade Fluorescence Signal Amplification Method for Factor XIa Inhibitor Screening.Anal Chem. 2024 Oct 8;96(40):16091-16098. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c04369. Epub 2024 Sep 28. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39340422
-
The mechanism underlying activation of factor IX by factor XIa.Thromb Res. 2014 May;133 Suppl 1(0 1):S48-51. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2014.03.020. Thromb Res. 2014. PMID: 24759143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the discovery and development of factor XI/XIa inhibitors.Med Res Rev. 2018 Sep;38(6):1974-2023. doi: 10.1002/med.21503. Epub 2018 May 4. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29727017 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coming soon to a pharmacy near you? FXI and FXII inhibitors to prevent or treat thromboembolism.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2022 Dec 9;2022(1):495-505. doi: 10.1182/hematology.2022000386. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2022. PMID: 36485148 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical Characterization of Novel DNA Aptamers against K103N/Y181C Double Mutant HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase.Molecules. 2022 Jan 3;27(1):285. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010285. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35011517 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of the Therapeutic Potential of Aptamers Targeting Coagulation Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 9;22(8):3897. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083897. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33918821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Mini-Review: Clinical Development and Potential of Aptamers for Thrombotic Events Treatment and Monitoring.Biomedicines. 2019 Jul 26;7(3):55. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines7030055. Biomedicines. 2019. PMID: 31357413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma contact factors as therapeutic targets.Blood Rev. 2018 Nov;32(6):433-448. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Blood Rev. 2018. PMID: 30075986 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

