In Situ Evaluation of Estrogen Receptor Dimers in Breast Carcinoma Cells: Visualization of Protein-Protein Interactions
- PMID: 28522883
- PMCID: PMC5433938
- DOI: 10.1267/ahc.17011
In Situ Evaluation of Estrogen Receptor Dimers in Breast Carcinoma Cells: Visualization of Protein-Protein Interactions
Abstract
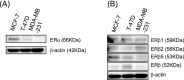
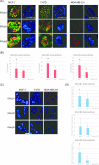
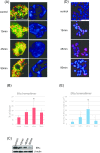
The estrogen receptor (ER) functions as a dimer and is involved in several different biological functions. However ER dimeric proteins have not been identified by in situ methodologies. Structured illumination microscopy (SIM) has been recently developed, which enabled the localization of protein and protein interaction. Therefore, in this study, we firstly demonstrated that ERs formed both homodimers and heterodimers in breast carcinoma cell lines using Nikon's SIM (N-SIM). ERα/α homodimers were detected in the nuclei of both ERα-positive MCF-7 and T-47D cells; 23.0% and 13.4% of ERα proteins formed ERα/α homodimers, respectively. ERα/β heterodimers were also detected in MCF-7 and T-47D. Approximately 6.6% of both ERα and ERβ1 proteins formed ERα/β1 heterodimers in MCF-7. In addition, 18.1% and 22.4% of ERα and ERβ proteins formed ERα/β2 heterodimers and ERα/β5 heterodimers in MCF-7, respectively. In addition, by using proximity ligation assay (PLA) in MCF-7, estradiol-induced ERα/α homodimers and ERα/β1 heterodimers were both detected after 15 to 45 min of treatment and at 15 min, respectively. The percentage of total ER proteins could also be determined using N-SIM. By using both methods, it has become possible to evaluate precise localization and ratio of ER dimers among different cell types.
Keywords: breast cancer; estrogen receptor dimer; protein-protein interaction; proximity ligation assay; structured illumination microscopy.
Figures


References
-
- Bai Y. and Giguére V. (2003) Isoform-selective interactions between estrogen receptors and steroid receptor coactivators promoted by estradiol and ErbB-2 signaling in living cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 17; 589–599. - PubMed
-
- Batmunkh B., Choijookhuu N., Srisowanna N., Byambatsogt U., Synn Oo. P., Noor Ali, M., Yamaguchi Y. and Hishikawa Y. (2017) Estrogen accelerates cell proliferation through estrogen receptor α during rat liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 50; 39–48. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chantzi N. I., Tiniakos D. G., Palaiologou M., Goutas N., Filippidis T., Vassilaros D. S., Dhimolea E., Mitsiou J. D. and Alexis N. M. (2013) Estrogen receptor beta 2 is associated with poor prognosis in estrogen receptor alpha-negative breast carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 139; 1489–1498. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cowley S. M., Hoare S., Mosselman S. and Parker M. G. (1997) Estrogen receptors alpha and beta form heterodimers on DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 272; 19858–19862. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

