Oxidative stress, antioxidants and intestinal calcium absorption
- PMID: 28522903
- PMCID: PMC5413780
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i16.2841
Oxidative stress, antioxidants and intestinal calcium absorption
Abstract
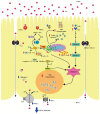
The disequilibrium between the production of reactive oxygen (ROS) and nitrogen (RNS) species and their elimination by protective mechanisms leads to oxidative stress. Mitochondria are the main source of ROS as by-products of electron transport chain. Most of the time the intestine responds adequately against the oxidative stress, but with aging or under conditions that exacerbate the ROS and/or RNS production, the defenses are not enough and contribute to developing intestinal pathologies. The endogenous antioxidant defense system in gut includes glutathione (GSH) and GSH-dependent enzymes as major components. When the ROS and/or RNS production is exacerbated, oxidative stress occurs and the intestinal Ca2+ absorption is inhibited. GSH depleting drugs such as DL-buthionine-S,R-sulfoximine, menadione and sodium deoxycholate inhibit the Ca2+ transport from lumen to blood by alteration in the protein expression and/or activity of molecules involved in the Ca2+ transcellular and paracellular pathways through mechanisms of oxidative stress, apoptosis and/or autophagy. Quercetin, melatonin, lithocholic and ursodeoxycholic acids block the effect of those drugs in experimental animals by their antioxidant, anti-apoptotic and/or anti-autophagic properties. Therefore, they may become drugs of choice for treatment of deteriorated intestinal Ca2+ absorption under oxidant conditions such as aging, diabetes, gut inflammation and other intestinal disorders.
Keywords: DL-buthionine-S,R-sulfoximine; Lithocholic acid; Melatonin; Menadione; Sodium deoxycholate; Transcellular and paracellular Ca2+pathways; Ursodeoxycholic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glutathione depleting drugs, antioxidants and intestinal calcium absorption.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov 28;24(44):4979-4988. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i44.4979. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30510373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium deoxycholate inhibits chick duodenal calcium absorption through oxidative stress and apoptosis.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2012 Aug;162(4):397-405. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.04.016. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22561666
-
l-Glutamine Attenuates Apoptosis in Porcine Enterocytes by Regulating Glutathione-Related Redox Homeostasis.J Nutr. 2018 Apr 1;148(4):526-534. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxx062. J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29659951
-
Glutamine protects intestinal calcium absorption against oxidative stress and apoptosis.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2017 Oct;212:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.07.006. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28732794
-
Molecular aspects of intestinal calcium absorption.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun 21;21(23):7142-54. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7142. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26109800 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal Ca2+ absorption revisited: A molecular and clinical approach.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jun 28;26(24):3344-3364. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i24.3344. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32655262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Tea, A Medicinal Food with Promising Neurological Benefits.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(3):349-359. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200529152625. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32469701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-Oxidative Effect of KIO3 and Protective Effect of Melatonin in the Thyroid-Comparison to Other Tissues.Life (Basel). 2021 Jun 21;11(6):592. doi: 10.3390/life11060592. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34205777 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoid Extract from Seed Residues of Hippophae rhamnoides ssp. sinensis Protects against Alcohol-Induced Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction by Regulating the Nrf2 Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Feb 24;12(3):562. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030562. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978810 Free PMC article.
-
Soybean Flour Fortified with Gryllus assimilis Powder to Increase Iron Bioavailability Improves Gut Health and Oxidative Balance In Vivo.Nutrients. 2025 Jan 25;17(3):437. doi: 10.3390/nu17030437. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boccatonda A, Tripaldi R, Davì G, Santilli F. Oxidative Stress Modulation Through Habitual Physical Activity. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22:3648–3680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

