Protein-losing pseudomembranous colitis with cap polyposis-like features
- PMID: 28522919
- PMCID: PMC5413796
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i16.3003
Protein-losing pseudomembranous colitis with cap polyposis-like features
Abstract
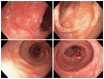
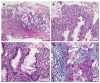
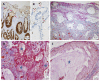
Protein-losing enteropathy (PLE) is characterized by loss of serum proteins into the gastrointestinal tract. It may lead to hypoproteinemia and clinically present as protein deficiency edema, ascites, pleural or pericardial effusion and/or malnutrition. In most cases the site of protein loss is the small intestine. Here we present an unusual case of severe PLE in a 55-year old female with a one-year history of recurrent diarrhea, crampy abdominal pain, and peripheral edema. Endoscopy and MRI showed a diffuse inflammatory thickening of the sigmoid colon and the rectum. Surgical resection of the involved colon was performed and the symptoms were significantly resolved. The final histologic evaluation confirmed a diagnosis of a pseudomembranous colitis with cap polyposis-like features. Such a cause of PLE has never been described before.
Keywords: Cap polyposis; Goblet cells; Protein-losing enteropathy; Pseudomembranes; Ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: There was no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Milovic V, Grand RJ. Protein-losing gastroenteropathy - UpToDate. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/protein-losing-gastroenteropathy.
-
- Aslam N, Wright R. Protein-Losing Enteropathy: Background, Pathophysiology, Etiology. (2016) Available from: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/182565-overview.
-
- Kovaleva V, Geissler AL, Lutz L, Fritsch R, Makowiec F, Wiesemann S, Hopt UT, Passlick B, Werner M, Lassmann S. Spatio-temporal mutation profiles of case-matched colorectal carcinomas and their metastases reveal unique de novo mutations in metachronous lung metastases by targeted next generation sequencing. Mol Cancer. 2016;15:63. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0549-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

