From Chaos to Harmony: Responses and Signaling upon Microbial Pattern Recognition
- PMID: 28525309
- PMCID: PMC6240913
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080516-035649
From Chaos to Harmony: Responses and Signaling upon Microbial Pattern Recognition
Abstract
Pathogen- or microbe-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs/MAMPs) are detected as nonself by host pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and activate pattern-triggered immunity (PTI). Microbial invasions often trigger the production of host-derived endogenous signals referred to as danger- or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which are also perceived by PRRs to modulate PTI responses. Collectively, PTI contributes to host defense against infections by a broad range of pathogens. Remarkable progress has been made toward demonstrating the cellular and physiological responses upon pattern recognition, elucidating the molecular, biochemical, and genetic mechanisms of PRR activation, and dissecting the complex signaling networks that orchestrate PTI responses. In this review, we present an update on the current understanding of how plants recognize and respond to nonself patterns, a process from which the seemingly chaotic responses form into a harmonic defense.
Keywords: damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs); microbial elicitors; pathogen- or microbe-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs or MAMPs); pattern recognition receptors (PRRs); pattern-triggered immunity (PTI); plant defense.
Figures


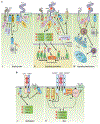
References
-
- Ahuja I, Kissen R, Bones AM. 2012. Phytoalexins in defense against pathogens. Trends Plant Sci 17:73–90 - PubMed
-
- Akamatsu A, Wong HL, Fujiwara M, Okuda J, Nishide K, et al. 2013. An OsCEBiP/OsCERK1-OsRacGEF1-OsRac1 module is an essential early component of chitin-induced rice immunity. Cell Host Microbe 13:465–76 - PubMed
-
- Albert I, Bohm H, Albert M, Feiler CE, Imkampe J, et al. 2015. An RLP23-SOBIR1-BAK1 complex mediates NLP-triggered immunity. Nat. Plants 1:15140. - PubMed
-
- Arnaud D, Hwang I. 2014. A sophisticated network of signaling pathways regulates stomatal defenses to bacterial pathogens. Mol. Plant 8:566–81 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

