Lymphocyte density determined by computational pathology validated as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: secondary analysis of the ARTemis trial
- PMID: 28525534
- PMCID: PMC5834010
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdx266
Lymphocyte density determined by computational pathology validated as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: secondary analysis of the ARTemis trial
Abstract
Background: We have previously shown lymphocyte density, measured using computational pathology, is associated with pathological complete response (pCR) in breast cancer. The clinical validity of this finding in independent studies, among patients receiving different chemotherapy, is unknown.
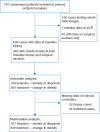
Patients and methods: The ARTemis trial randomly assigned 800 women with early stage breast cancer between May 2009 and January 2013 to three cycles of docetaxel, followed by three cycles of fluorouracil, epirubicin and cyclophosphamide once every 21 days with or without four cycles of bevacizumab. The primary endpoint was pCR (absence of invasive cancer in the breast and lymph nodes). We quantified lymphocyte density within haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) whole slide images using our previously described computational pathology approach: for every detected lymphocyte the average distance to the nearest 50 lymphocytes was calculated and the density derived from this statistic. We analyzed both pre-treatment biopsies and post-treatment surgical samples of the tumour bed.
Results: Of the 781 patients originally included in the primary endpoint analysis of the trial, 609 (78%) were included for baseline lymphocyte density analyses and a subset of 383 (49% of 781) for analyses of change in lymphocyte density. The main reason for loss of patients was the availability of digitized whole slide images. Pre-treatment lymphocyte density modelled as a continuous variable was associated with pCR on univariate analysis (odds ratio [OR], 2.92; 95% CI, 1.78-4.85; P < 0.001) and after adjustment for clinical covariates (OR, 2.13; 95% CI, 1.24-3.67; P = 0.006). Increased pre- to post-treatment lymphocyte density showed an independent inverse association with pCR (adjusted OR, 0.1; 95% CI, 0.033-0.31; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Lymphocyte density in pre-treatment biopsies was validated as an independent predictor of pCR in breast cancer. Computational pathology is emerging as a viable and objective means of identifying predictive biomarkers for cancer patients.
Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT01093235.
Keywords: breast cancer; computational pathology; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; predictive; tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology.
Figures
References
-
- Earl HM, Vallier AL, Hiller L. et al. Effects of the addition of gemcitabine, and paclitaxel-first sequencing, in neoadjuvant sequential epirubicin, cyclophosphamide, and paclitaxel for women with high-risk early breast cancer (Neo-tAnGo): an open-label, 2x2 factorial randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2014; 15(2): 201–212. - PubMed
-
- Earl HM, Hiller L, Dunn JA. et al. Efficacy of neoadjuvant bevacizumab added to docetaxel followed by fluorouracil, epirubicin, and cyclophosphamide, for women with HER2-negative early breast cancer (ARTemis): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16(6): 656–666. - PubMed
-
- Earl HM, Hiller L, Dunn JA. et al. Disease-free and overall survival at 3.5 years for neoadjuvant bevacizumab added to docetaxel followed by fluorouracil, epirubicin and cyclophosphamide, for women with HER2 negative early breast cancer: ARTemis Trial. Ann Oncol 2017; 28(8): 1817–1824. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

