Widespread Influence of 3'-End Structures on Mammalian mRNA Processing and Stability
- PMID: 28525757
- PMCID: PMC5546744
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.036
Widespread Influence of 3'-End Structures on Mammalian mRNA Processing and Stability
Abstract
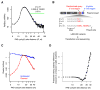
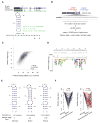
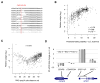
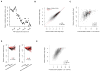
The physiological relevance of structures within mammalian mRNAs has been elusive, as these mRNAs are less folded in cells than in vitro and have predicted secondary structures no more stable than those of random sequences. Here, we investigate the possibility that mRNA structures facilitate the 3'-end processing of thousands of human mRNAs by juxtaposing poly(A) signals (PASs) and cleavage sites that are otherwise too far apart. We find that RNA structures are predicted to be more prevalent within these extended 3'-end regions than within PAS-upstream regions and indeed are substantially more folded within cells, as determined by intracellular probing. Analyses of thousands of ectopically expressed variants demonstrate that this folding both enhances processing and increases mRNA metabolic stability. Even folds with predicted stabilities resembling those of random sequences can enhance processing. Structure-controlled processing can also regulate neighboring gene expression. Thus, RNA structure has widespread roles in mammalian mRNA biogenesis and metabolism.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; DMS-seq; RNA metabolic labeling; cleavage and polyadenylation; high-throughput analysis; in vivo structural probing; mRNA 3′ end processing; mRNA stability; mRNA structure.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed YF, Gilmartin GM, Hanly SM, Nevins JR, Greene WC. The HTLV-I Rex response element mediates a novel form of mRNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1991;64:727–737. - PubMed
-
- Brown PH, Tiley LS, Cullen BR. Effect of RNA secondary structure on polyadenylation site selection. Genes Dev. 1991;5:1277–1284. - PubMed
-
- Chan SW, Fowler KJ, Choo KHA, Kalitsis P. Spef1, a conserved novel testis protein found in mouse sperm flagella. Gene. 2005;353:189–199. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

