Management of rare diseases of the Head, Neck and Teeth: results of a French population-based prospective 8-year study
- PMID: 28526043
- PMCID: PMC5437557
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-017-0650-0
Management of rare diseases of the Head, Neck and Teeth: results of a French population-based prospective 8-year study
Abstract
Background: In the last ten years, national rare disease networks have been established in France, including national centres of expertise and regional ones, with storage of patient data in a bioinformatics tool. The aim was to contribute to the development and evaluation of health strategies to improve the management of patients with rare diseases. The objective of this study has been to provide the first national-level data concerning rare diseases of the head, neck and teeth and to assess the balance between demand and supply of care in France.
Methods: Centres of expertise for rare diseases record a minimum data set on their clinical cases, using a list of rare Head, Neck and Teeth diseases established in 2006. The present analysis focuses on 2008 to 2015 data based on the Orphanet nomenclature. Each rare disease RD "case" was defined by status "affected" and by the degree of diagnostic certainty, encoded as: confirmed, probable or non-classifiable. Analysed parameters, presented with their 95% confidence intervals using a Poisson model, were the following: time and age at diagnosis, proportions of crude and standardized RD prevalence by age, gender and geographical site. The criteria studied were the proportions of patients in Paris Region and the "included cases geography", in which these proportions were projected onto the other French Regions, adjusting for local populations.
Results: In Paris Region, estimated prevalence of these diseases was 5.58 per 10,000 inhabitants (95% CI 4.3-7.1). At December 31st 2015, 11,342 patients were referenced in total in France, of whom 7294 were in Paris Region. More than 580 individual clinical entities (ORPHA code) were identified with their respective frequencies. Most abnormalities were diagnosed antenatally. Nearly 80% of patients recorded come to Paris hospitals to obtain either diagnosis, care or follow up. We observed that the rarer the disease, the more patients were referred to Paris hospitals.
Conclusions: A health network covering a range of aspects of the rare diseases problematic from diagnostics to research has been developed in France. Despite this, there is still a noticeable imbalance between health care supply and demand in this area.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Oral cleft; Orofacial diseases; Rare diseases; Registry.
Figures
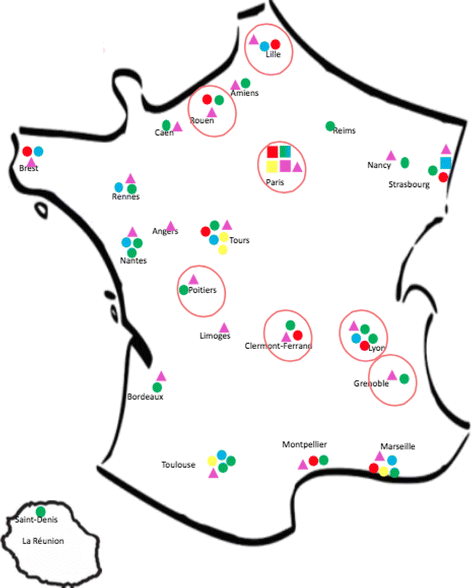
 CEMARA USERS.
CEMARA USERS.  Reference centers.
Reference centers.  Severe ENT Malformations competence centers.
Severe ENT Malformations competence centers.  Severe Craniofacial malformations competence centers.
Severe Craniofacial malformations competence centers.  Cleft lip and palate competence centers.
Cleft lip and palate competence centers.  Rare dental Malformations competence centers.
Rare dental Malformations competence centers.  Reference centers “Pierre Robin”
Reference centers “Pierre Robin”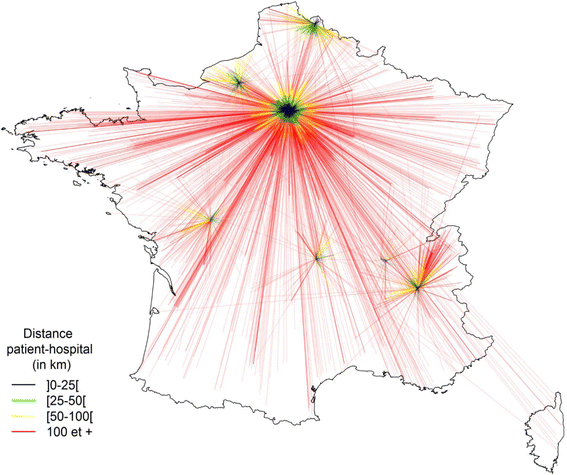
 ] 0-25 [.
] 0-25 [.  ] 25-50 [.
] 25-50 [.  ] 50-100 [.
] 50-100 [.  100 and more
100 and moreSimilar articles
-
Italian cancer figures--Report 2015: The burden of rare cancers in Italy.Epidemiol Prev. 2016 Jan-Feb;40(1 Suppl 2):1-120. doi: 10.19191/EP16.1S2.P001.035. Epidemiol Prev. 2016. PMID: 26951748
-
Overview of patients' cohorts in the French National rare disease registry.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2023 Jul 3;18(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s13023-023-02725-2. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2023. PMID: 37400917 Free PMC article.
-
Italian cancer figures, report 2012: Cancer in children and adolescents.Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Jan-Feb;37(1 Suppl 1):1-225. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23585445 English, Italian.
-
[SENTIERI - Epidemiological Study of Residents in National Priority Contaminated Sites. Sixth Report].Epidemiol Prev. 2023 Jan-Apr;47(1-2 Suppl 1):1-286. doi: 10.19191/EP23.1-2-S1.003. Epidemiol Prev. 2023. PMID: 36825373 Italian.
-
Surgical removal versus retention for the management of asymptomatic disease-free impacted wisdom teeth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 4;5(5):CD003879. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003879.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32368796 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Determinants of dental care use in patients with rare diseases: a qualitative exploration.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Jun 22;23(1):413. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03048-1. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37349716 Free PMC article.
-
Consideration of oral health in rare disease expertise centres: a retrospective study on 39 rare diseases using text mining extraction method.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Aug 20;17(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02467-7. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 35987771 Free PMC article.
-
10 years of CEMARA database in the AnDDI-Rares network: a unique resource facilitating research and epidemiology in developmental disorders in France.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021 Aug 4;16(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s13023-021-01957-4. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021. PMID: 34348744 Free PMC article.
-
Global birth prevalence of Robin sequence in live-born infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Respir Rev. 2023 Dec 6;32(170):230133. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0133-2023. Print 2023 Dec 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2023. PMID: 38056889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Richter T, Nestler-Parr S, Babela R, Khan ZM, Tesoro T, Molsen E, HDIS for P and ORRDSIG. Rare Disease Terminology and Definitions—A Systematic Global Review: Report of the ISPOR Rare Disease Special Interest Group. - PubMed
-
- Boycott KM. Depth of the rare genetic diseases: strategies to identify the remaining genes and diseases. Pathology. 2016;48. http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/ejhg.2016.146. - DOI
-
- Orphanet Report Series - Prevalence of rare diseases: Bibliographic data - November 2016 - Number 1 http://www.orpha.net/orphacom/cahiers/docs/GB/Prevalence_of_rare_disease.... 2016.
-
- de La Dure-Molla M, Philippe Fournier B, Berdal A. Isolated dentinogenesis imperfecta and dentin dysplasia: revision of the classification. Eur J Hum Genet [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2017 Jan 2];23:445–51. Available from: http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/ejhg.2014.159 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kortelainen T, Tolvanen M, Luoto A, Ylikontiola LP, Sándor GK, Lahti S. Comparison of Oral Health–Related Quality of Life Among Schoolchildren With and Without Cleft Lip and/or Palate. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2016 Nov 3];53:e172–6. Available from: http://www.cpcjournal.org/doi/10.1597/14-180 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

