Targeting the CXCR4 pathway using a novel anti-CXCR4 IgG1 antibody (PF-06747143) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- PMID: 28526063
- PMCID: PMC5438492
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-017-0435-x
Targeting the CXCR4 pathway using a novel anti-CXCR4 IgG1 antibody (PF-06747143) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Abstract
Background: The CXCR4-CXCL12 axis plays an important role in the chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)-microenvironment interaction. Overexpression of CXCR4 has been reported in different hematological malignancies including CLL. Binding of the pro-survival chemokine CXCL12 with its cognate receptor CXCR4 induces cell migration. CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling axis promotes cell survival and proliferation and may contribute to the tropism of leukemia cells towards lymphoid tissues and bone marrow. Therefore, we hypothesized that targeting CXCR4 with an IgG1 antibody, PF-06747143, may constitute an effective therapeutic approach for CLL.
Methods: Patient-derived primary CLL-B cells were assessed for cytotoxicity in an in vitro model of CLL microenvironment. PF-06747143 was analyzed for cell death induction and for its potential to interfere with the chemokine CXCL12-induced mechanisms, including migration and F-actin polymerization. PF-06747143 in vivo efficacy was determined in a CLL murine xenograft tumor model.
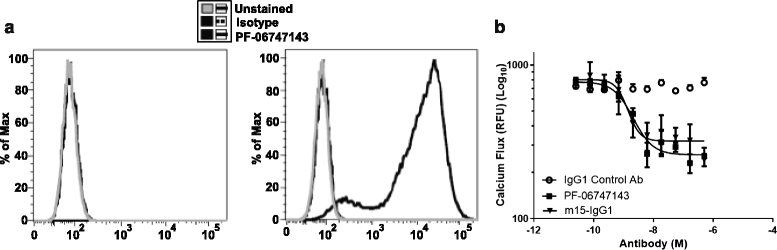
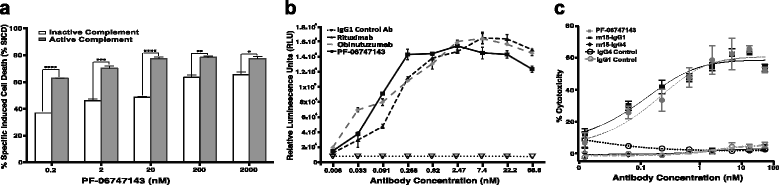
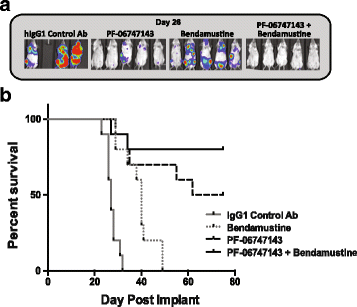
Results: PF-06747143, a novel-humanized IgG1 CXCR4 antagonist antibody, induced cell death of patient-derived primary CLL-B cells, in presence or absence of stromal cells. Moreover, cell death induction by the antibody was independent of CLL high-risk prognostic markers. The cell death mechanism was dependent on CXCR4 expression, required antibody bivalency, involved reactive oxygen species production, and did not require caspase activation, all characteristics reminiscent of programmed cell death (PCD). PF-06747143 also induced potent B-CLL cytotoxicity via Fc-driven antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity activity (CDC). PF-06747143 had significant combinatorial effect with standard of care (SOC) agents in B-CLL treatment, including rituximab, fludarabine (F-ara-A), ibrutinib, and bendamustine. In a CLL xenograft model, PF-06747143 decreased tumor burden and improved survival as a monotherapy, and in combination with bendamustine.
Conclusions: We show evidence that PF-06747143 has biological activity in CLL primary cells, supporting a rationale for evaluation of PF-06747143 for the treatment of CLL patients.
Keywords: ADCC; CDC; CXCL12; CXCR4; Cell death; Chemokine; Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; PF-06747143; Reactive oxygen species.
Figures





References
-
- Burger M, Hartmann T, Krome M, Rawluk J, Tamamura H, Fujii N, Kipps TJ, Burger JA. Small peptide inhibitors of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor (CD184) antagonize the activation, migration, and antiapoptotic responses of CXCL12 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Blood. 2005;106(5):1824–30. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-12-4918. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

