XLF-mediated NHEJ activity in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy resistance
- PMID: 28526069
- PMCID: PMC5437682
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3345-y
XLF-mediated NHEJ activity in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy resistance
Abstract
Background: DNA repair pathways are used by cancer cells to overcome many standard anticancer treatments, causing therapy resistance. Here, we investigated the role of XRCC4-like factor (XLF), a core member of the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair pathway, in chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: qRT-PCR analysis and western blotting were performed to detect expression levels of genes and proteins related to NHEJ. NHEJ repair capacity was assessed in vitro (cell-free) and in vivo by monitoring the activity of the NHEJ pathway. Cell viability and IC50 assays were used to measure sensitivity to drug therapy. A xenograft HCC model was used to develop methods of targeting XLF-induced chemosensitization. Clinicopathological analysis was conducted on patients with HCC treated with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
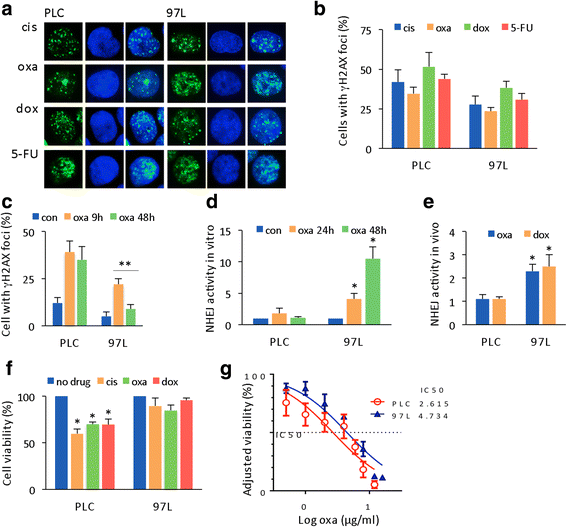
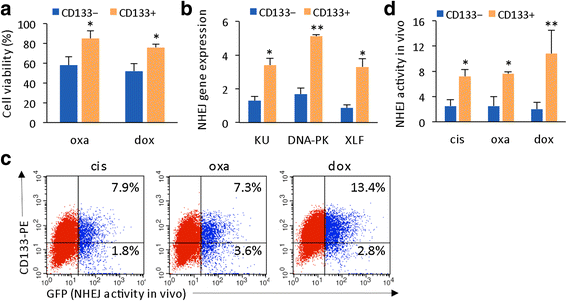
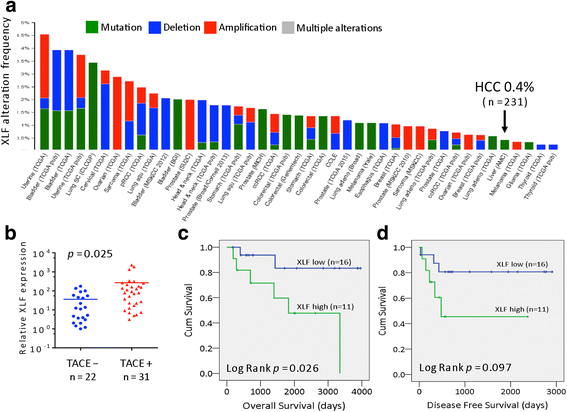
Results: Many conventional cancer chemotherapeutics induce DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). HCC cells respond to these breaks by increasing their NHEJ activity, resulting in resistance. XLF-knockdown cells show an inhibition of NHEJ activity in both cell-free and live-cell assays as well as a high level of unrepaired cellular DSBs. These results indicate that XLF facilitates DNA end-joining and therefore promotes NHEJ activity in cancer cells. Consequently, knockdown of XLF significantly chemosensitized resistant cells both in vitro and in xenograft tumors. A low rate of XLF genomic alteration was found in patients with primary HCC, but XLF expression was induced after drug treatment. Clinically, a high level of XLF expression is significantly associated with advanced HCC and shorter overall survival.
Conclusion: Chemotherapy-induced overexpression of XLF and XLF-mediated enhancements in NHEJ activity contribute to chemoresistance in HCC cells and patients with HCC. Targeting XLF to modulate DSB repair could enhance drug sensitivity and may be a therapeutically useful addition to conventional therapy.
Keywords: Chemoresistance; DNA repair; HCC; NHEJ activity; XLF.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PAXX and XLF DNA repair factors are functionally redundant in joining DNA breaks in a G1-arrested progenitor B-cell line.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 20;113(38):10619-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611882113. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27601633 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic interaction between DNA repair factors PAXX, XLF, XRCC4 and DNA-PKcs in human cells.FEBS Open Bio. 2019 Jul;9(7):1315-1326. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12681. Epub 2019 Jun 12. FEBS Open Bio. 2019. PMID: 31141305 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of XLF and PAXX prevents DNA double-strand break repair by non-homologous end joining in lymphocytes.Cell Cycle. 2017 Feb;16(3):286-295. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1253640. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 27830975 Free PMC article.
-
Cernunnos/XLF: a new player in DNA double-strand break repair.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 Jun;41(6):1237-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Oct 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 18992362 Review.
-
XRCC4 and XLF form long helical protein filaments suitable for DNA end protection and alignment to facilitate DNA double strand break repair.Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;91(1):31-41. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2012-0058. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23442139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of HMGB1 in Cisplatin-Persistent Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 13;11:750677. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.750677. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34966671 Free PMC article.
-
PAXX, Not NHEJ1 Is an Independent Prognosticator in Colon Cancer.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Oct 23;7:584053. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.584053. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33195430 Free PMC article.
-
Doxorubicin-Induced Translocation of mtDNA into the Nuclear Genome of Human Lymphocytes Detected Using a Molecular-Cytogenetic Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 17;21(20):7690. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207690. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33080837 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of HMGB1 Overcomes Resistance to Radiation and Chemotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 May 14;13:4189-4199. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S239243. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32523355 Free PMC article.
-
DNA repair and the contribution to chemotherapy resistance.Genome Med. 2025 May 26;17(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13073-025-01488-8. Genome Med. 2025. PMID: 40420317 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

