Differences in serum and synovial CD4+ T cells and cytokine profiles to stratify patients with inflammatory osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 28526072
- PMCID: PMC5437517
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-017-1305-1
Differences in serum and synovial CD4+ T cells and cytokine profiles to stratify patients with inflammatory osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: The aim was to investigate CD4+T-cell subsets, immune cells and their cytokine profiles in blood and synovial compartments in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and inflammatory osteoarthritis (OA) to define specific immune signatures.
Methods: Peripheral blood, synovial fluid (SF) and synovial membranes (SM) of RA and OA patients were analyzed. CD4+T-cell subset frequencies were determined by flow cytometry, and cytokine concentrations in serum and SF were measured by ELISA.
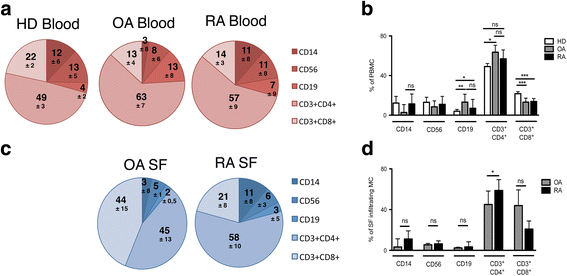
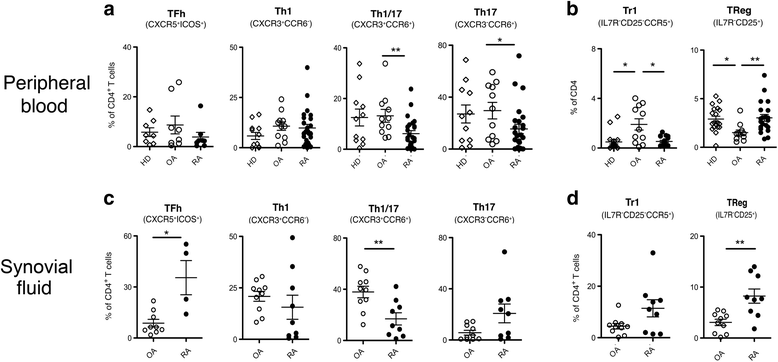
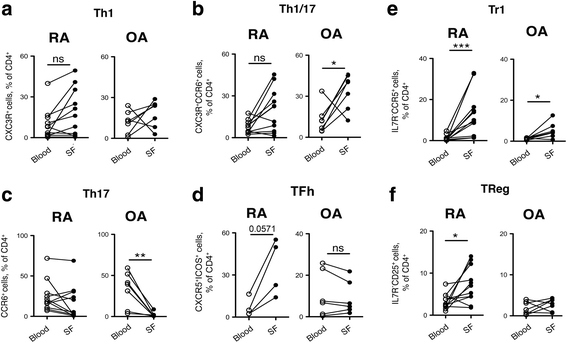
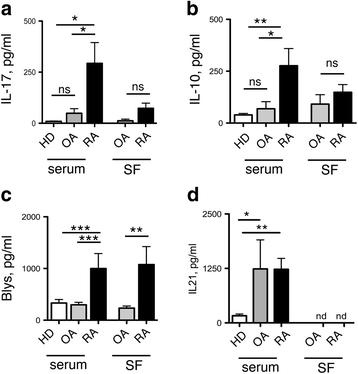
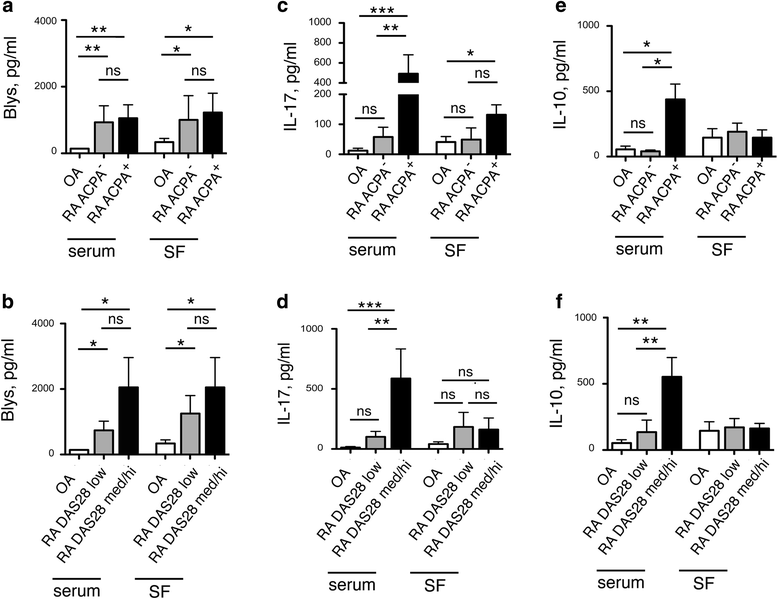
Results: In peripheral blood, OA patients had altered frequencies of regulatory T-cell subsets, and higher frequencies of Th17 and of Th1/17 cells than RA patients. In the synovial compartment of OA patients, conventional Th17 cells were largely excluded, while Th1/17 cells were enriched and more frequent than in RA patients. Conversely, in the synovial compartment of RA patients, regulatory T cells and Tfh cells were enriched and more frequent then in OA patients. IL-17 and Blys were increased both in serum and SF of RA patients, and correlated with autoantibodies and disease activity. Notably, Blys levels were already significantly elevated in RA patients with low disease activity score in 28 joints (DAS28) and without autoantibody positivity.
Conclusions: Although patients with inflammatory OA have immune activation in the synovial compartment, they display different T-cell subset frequencies and cytokine profiles. Soluble mediators such as Blys might help to discriminate mild clinical forms of RA from inflammatory OA particularly at the onset of the disease.
Keywords: Blys; Cytokines; Inflammatory osteoarthritis; Rheumatoid arthritis; T helper subsets.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

