Soluble Axl is an accurate biomarker of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma development: results from a large scale multicenter analysis
- PMID: 28526812
- PMCID: PMC5542263
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17598
Soluble Axl is an accurate biomarker of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma development: results from a large scale multicenter analysis
Abstract
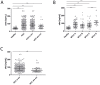
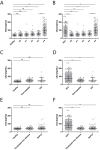
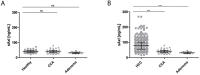
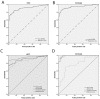
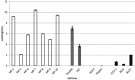
Patients with chronic liver disease (CLD) and cirrhosis are at high risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Current diagnostic tools for HCC detection include imaging techniques and serum biomarkers such as α-fetoprotein (AFP). Yet, these methods are limited in sensitivity and specificity to accurately detect early HCC. Here we focused on the potential of soluble Axl (sAxl) as a biomarker in CLD patients by analyzing serum samples of 1067 patients and healthy controls from centers in Europe and Asia. We show that serum concentrations of sAxl were significantly increased at early (82.57 ng/mL) and later stages of HCC (114.50 ng/mL) as compared to healthy controls (40.15 ng/mL). Notably, no elevated sAxl levels were detected in patients with CLD including chronic viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, cholestatic liver disease, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease versus healthy controls. Furthermore, sAxl did not rise in liver adenomas or cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). Yet, patients with advanced fibrosis (F3) or cirrhosis (F4) showed enhanced sAxl concentrations (F3: 54.67 ng/mL; F4: 94.74 ng/mL). Hepatic myofibroblasts exhibited an increased release of sAxl, suggesting that elevated sAxl levels arise from these cells during fibrosis. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of sAxl displayed a strongly increased sensitivity and specificity to detect both cirrhosis (80.8%/92.0%) and HCC (83.3%/86.7%) with an area under the curve of 0.935/0.903 as compared to AFP. In conclusion, sAxl shows high diagnostic accuracy at early stage HCC as well as cirrhosis, thereby outperforming AFP. Importantly, sAxl remains normal in most common CLDs, liver adenomas and CCA.
Keywords: biomarker; cirrhosis; fibrosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; soluble Axl.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–2576. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- Ikai I, Kudo M, Arii S, Omata M, Kojiro M, Sakamoto M, Takayasu K, Hayashi N, Makuuchi M, Matsuyama Y, Monden M. Report of the 18th follow-up survey of primary liver cancer in Japan. Hepatol Res. 2010;40:1043–1059. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Bustamante J, Castells A, Vilana R, Ayuso Mdel C, Sala M, Bru C, Rodes J, Bruix J. Natural history of untreated nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma: rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials. Hepatology. 1999;29:62–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

