Super-Enhancers and Broad H3K4me3 Domains Form Complex Gene Regulatory Circuits Involving Chromatin Interactions
- PMID: 28526829
- PMCID: PMC5438348
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02257-3
Super-Enhancers and Broad H3K4me3 Domains Form Complex Gene Regulatory Circuits Involving Chromatin Interactions
Abstract
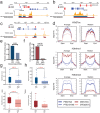
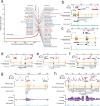
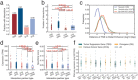
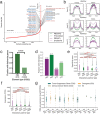
Stretched histone regions, such as super-enhancers and broad H3K4me3 domains, are associated with maintenance of cell identity and cancer. We connected super-enhancers and broad H3K4me3 domains in the K562 chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line as well as the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line with chromatin interactions. Super-enhancers and broad H3K4me3 domains showed higher association with chromatin interactions than their typical counterparts. Interestingly, we identified a subset of super-enhancers that overlap with broad H3K4me3 domains and show high association with cancer-associated genes including tumor suppressor genes. Besides cell lines, we could observe chromatin interactions by a Chromosome Conformation Capture (3C)-based method, in primary human samples. Several chromatin interactions involving super-enhancers and broad H3K4me3 domains are constitutive and can be found in both cancer and normal samples. Taken together, these results reveal a new layer of complexity in gene regulation by super-enhancers and broad H3K4me3 domains.
Conflict of interest statement
M.J.F. declares two patents on methodologies related to ChIA-PET. A.R., J.G., M.S., E.H. and A.A. are employees of Oxford Biodynamics Plc, a company based on chromatin interaction biomarkers and which owns patents on chromatin interaction analysis methods. No other conflicts of interest are declared.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

